疑问¶
- ampere 架构 SM 中有 4 个 process block,process block 对应一个 warp?意思是可以有 4 个 warp 同时执行?
- Femi 架构没有 process block,SM 就是最小单元?
- The threads of a thread block execute concurrently on one multiprocessor, and multiple thread blocks can execute concurrently on one multiprocessor.
- 这样岂不是若干 thread block 抢一个 SM 上的 shared memory?
- 不同 threadblock 的 warp 并发执行,如何隐藏延迟
- cuda 分块大小对性能影响很大,那么如何确定分块大小呢?
- 穷举
- 分析模型?
CUDA guide¶
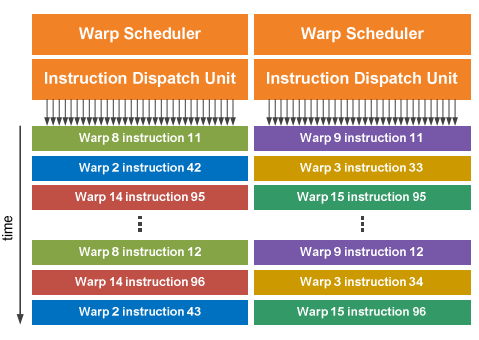
At every instruction issue time, a warp scheduler selects an instruction that is ready to execute. This instruction can be another independent instruction of the same warp, exploiting instruction-level parallelism, or more commonly an instruction of another warp, exploiting thread-level parallelism
he number of clock cycles it takes for a warp to be ready to execute its next instruction is called the latency, and full utilization is achieved when all warp schedulers always have some instruction to issue for some warp at every clock cycle during that latency period, or in other words, when latency is completely “hidden”. The number of instructions required to hide a latency of L clock cycles depends on the respective throughputs of these instructions (see Arithmetic Instructions for the throughputs of various arithmetic instructions). If we assume instructions with maximum throughput, it is equal to:
- 4L for devices of compute capability 5.x, 6.1, 6.2, 7.x and 8.x since for these devices, a multiprocessor issues one instruction per warp over one clock cycle for four warps at a time, as mentioned in Compute Capabilities.
- 2L for devices of compute capability 6.0 since for these devices, the two instructions issued every cycle are one instruction for two different warps.
On devices of compute capability 7.x, for most arithmetic instructions, it is typically 4 clock cycles. This means that 16 active warps per multiprocessor (4 cycles, 4 warp schedulers) are required to hide arithmetic instruction latencies (assuming that warps execute instructions with maximum throughput, otherwise fewer warps are needed). If the individual warps exhibit instruction-level parallelism, i.e. have multiple independent instructions in their instruction stream, fewer warps are needed because multiple independent instructions from a single warp can be issued back to back.
硬件单元¶
Throughput of Native Arithmetic Instructions. (Number of Results per Clock Cycle per Multiprocessor) CUDA C++ Programming Guide
2.x 后有的 Cache (i.e., L1 cache and L2 cache available on devices of compute capability 2.x and higher, texture cache and constant cache available on all devices).
cache 的应用场景:for which global memory access patterns are data-dependent
On devices of compute capability 5.x onwards, local memory accesses are always cached in L2 in the same way as global memory accesses
NV 架构列表¶
compute capacity¶
Matching CUDA arch and CUDA gencode for various NVIDIA architectures - Arnon Shimoni
- Pascal
- SM61: 1080
- volta
- SM70: Tesla V100, Titan V
- Ampere
- SM80: NVIDIA A100 (the name “Tesla” has been dropped – GA100))
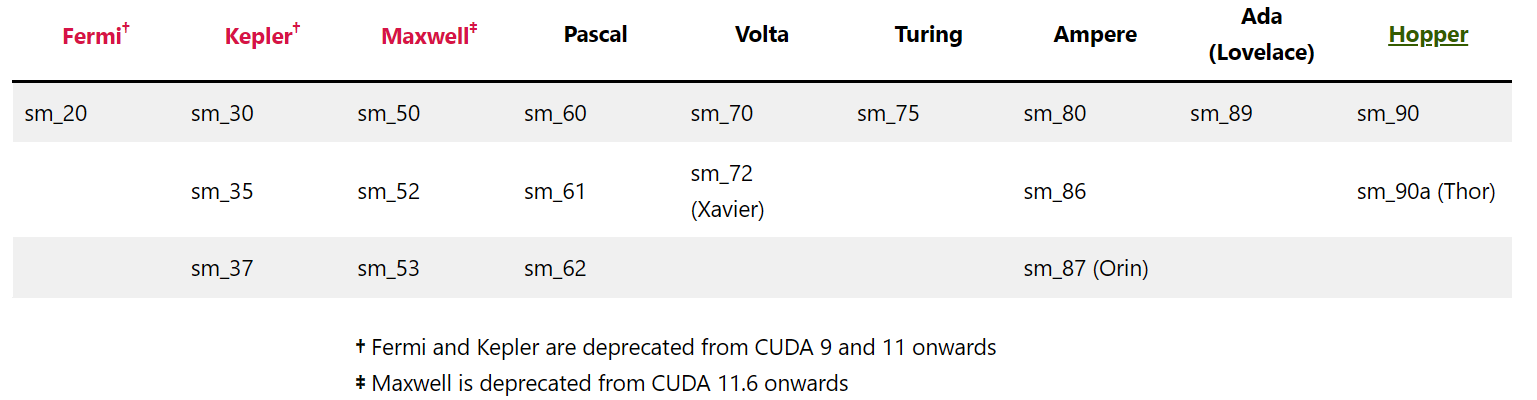
- SM80: NVIDIA A100 (the name “Tesla” has been dropped – GA100))
- Tesla(2008)
- Fermi(2010)
- Kepler(2012):K80
- Maxwell(2014): M10/M40
- Pascal(2016): Tesla P40、P100、GTX 1080Ti Titan XP、Quadro GP100/P6000/P5000,10系
- Volta(2017): Tesla V100、GeForce Titan V、Quadro GV100 专业卡
- Turing(2018):1 个 SM 8 个 Tensor core,1 个 RT core,16,20 系
- Ampere(2020): A100,30 系
- Hopper(2022):H100
1080: 20x128 1080ti: 28x128, gp104 p40: 30x128, gp102 p100: 28x128, HBM2(4096bit)
Ampere (microarchitecture) - Wikipedia
架构¶
NVIDIA GPU 架构梳理 - 知乎 (zhihu.com) NVIDIA GPU 架构演进 | Chenfan Blog
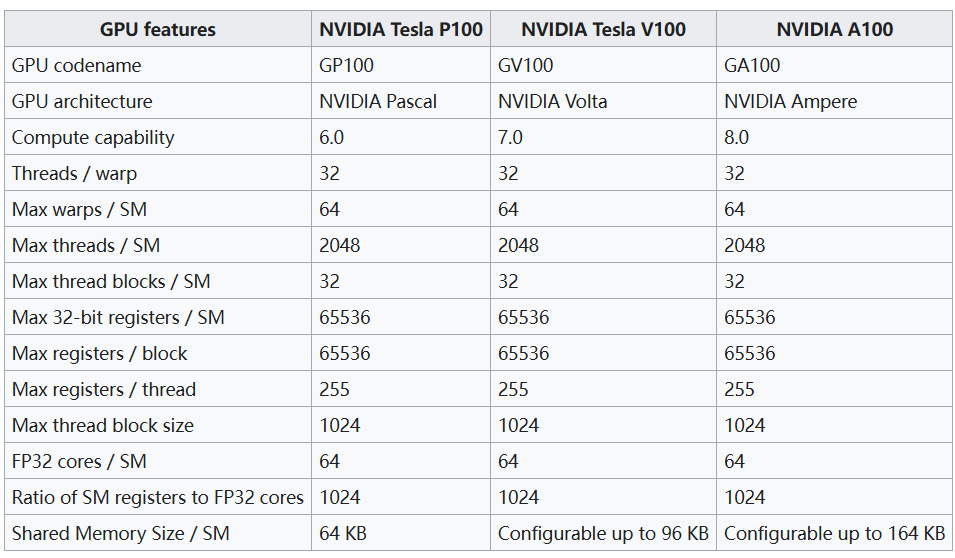
对比¶
- 来自 GCoM 论文,其中 volta cacheline 为 32 B,应该是写错了。
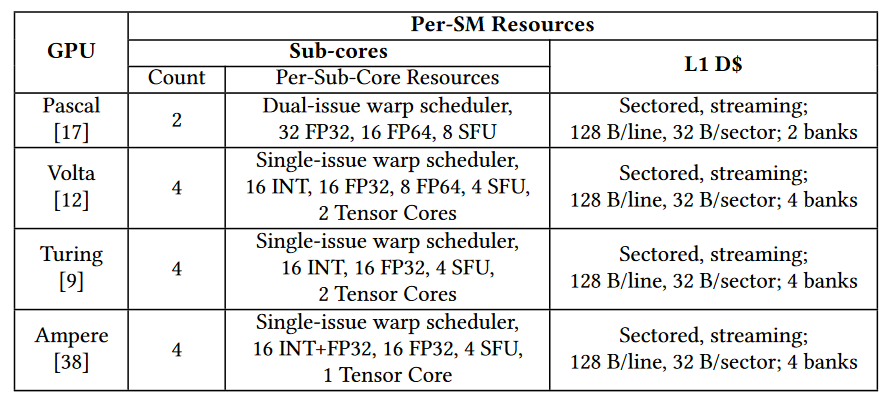
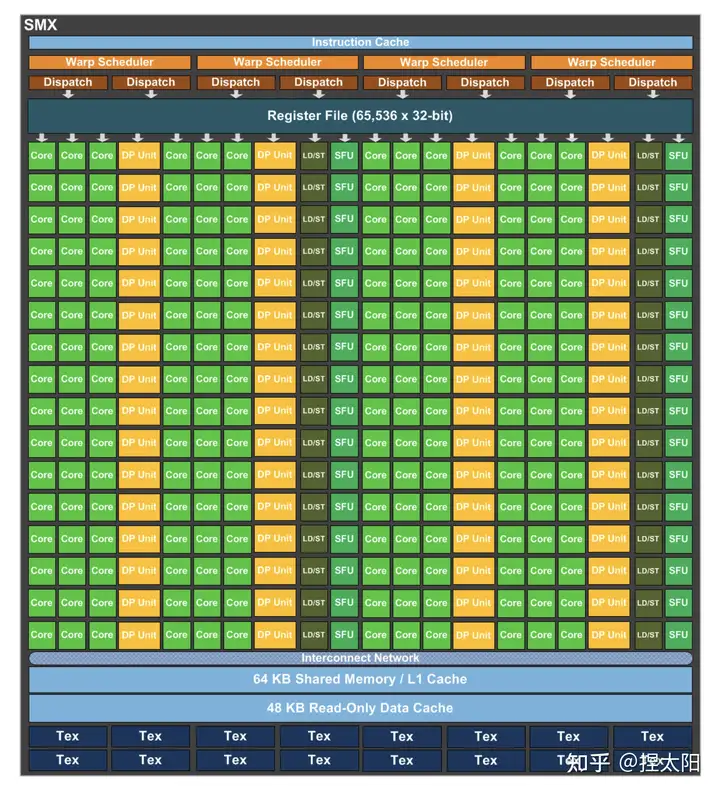
- Fermi:每个 GPC 包含 4 个 SM,每个 SM 包含 32 个 CUDA,2 个 warp scheduler(x1 dispatch)
- Kepler:SMX,一个 SMX 4 个 WS(x2 Dispatch),192 CUDA
- Maxwell: SMM,4 个 Process block(类似于 Fermi 的 SM),每个 process block 1 个 WS(x2 Dispatch)
寄存器数,基本都是一个 SM,65536(可以分成 4 个 16384,或者两个 32768)
- pascal,L1 $D 和 shared memory 都是分开的,turing 开始合并
- turing 去掉了对 FP64 的支持
术语¶
- GPC:费米为例,整个 GPU 有多个 GPC(图形处理集群),单个GPC包含一个光栅引擎(Raster Engine),四个 SM(流式多处理器),GPC 可以被认为是一个独立的 GPU。所有从 Fermi 开始的 NVIDIA GPU,都有 GPC。
- 核心是一个完整的GPU模组,如 GP100,GP102
Fermi¶
- 橙色部分:2 个 Warp Scheduler/Dispatch Unit
- 绿色部分:32 个 CUDA 内核,分在两条 lane 上,每条分别是 16 个
https://stackoverflow.com/a/10467342
The programmer divides work into threads, threads into thread blocks, and thread blocks into grids. The compute work distributor allocates thread blocks to Streaming Multiprocessors (SMs). Once a thread block is distributed to a SM the resources for the thread block are allocated (warps and shared memory) and threads are divided into groups of 32 threads called warps. Once a warp is allocated it is called an active warp. The two warp schedulers pick two active warps per cycle and dispatch warps to execution units. For more details on execution units and instruction dispatch see 1 p.7-10 and 2.
Fermi,一个 SM 有两个 warp 保证每周期有指令可以发射
A stalled warp is ineligible to be selected by the warp scheduler. On Fermi it is useful to have at least 2 eligible warps per cycle so that the warp scheduler can issue an instruction.
GeForce 560Ti,8SM,每个 48CUDA
If you launch kernel<<<8, 48>>> you will get 8 blocks each with 2 warps of 32 and 16 threads. There is no guarantee that these 8 blocks will be assigned to different SMs.
- 每个 SM 可以有很多线程块
A GTX560 can have 8 SM *8 blocks = 64 blocks at a time or 8 SM* 48 warps = 512 warps if the kernel does not max out registers or shared memory. At any given time on a portion of the work will be active on SMs. Each SM has multiple execution units (more than CUDA cores). Which resources are in use at any given time is dependent on the warp schedulers and instruction mix of the application. If you don't do TEX operations then the TEX units will be idle. If you don't do a special floating point operation the SUFU units will idle.

GF104 的超标量¶
GF104: NVIDIA Goes Superscalar - NVIDIA’s GeForce GTX 460: The $200 King
有三组 cuda block,但是只有两个 warp 调度器
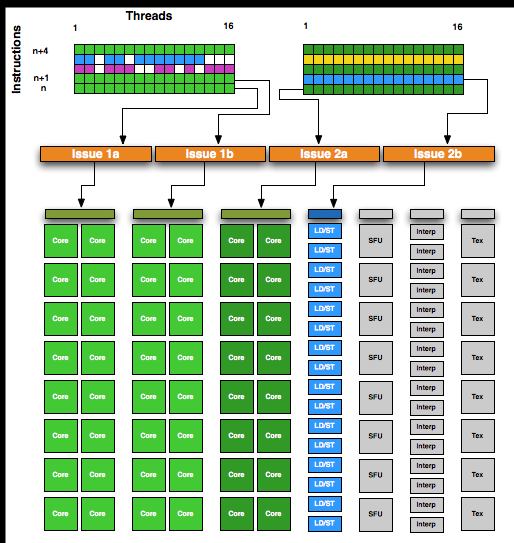
GF100 是 32 个 CUDA 每 SM
白皮书¶
Microsoft Word - NVIDIA Fermi Architecture Whitepaper.docx
双发射
Fermi’s dual warp scheduler selects two warps, and issues one instruction from each warp to a group of sixteen cores, sixteen load/store units, or four SFUs. Because warps execute independently, Fermi’s scheduler does not need to check for dependencies from within the instruction stream. Using this elegant model of dual-issue, Fermi achieves near peak hardware performance. Most instructions can be dual issued; two integer instructions, two floating instructions, or a mix of integer, floating point, load, store, and SFU instructions can be issued concurrently. Double precision instructions do not support dual dispatch with any other operation.
可配置的 shared memory 和 L1 cache
G80 and GT200 have 16 KB of shared memory per SM. In the Fermi architecture, each SM has 64 KB of on-chip memory that can be configured as 48 KB of Shared memory with 16 KB of L1 cache or as 16 KB of Shared memory with 48 KB of L1 cache.
Kepler¶
- 一个 SMX 192 个 CUDA
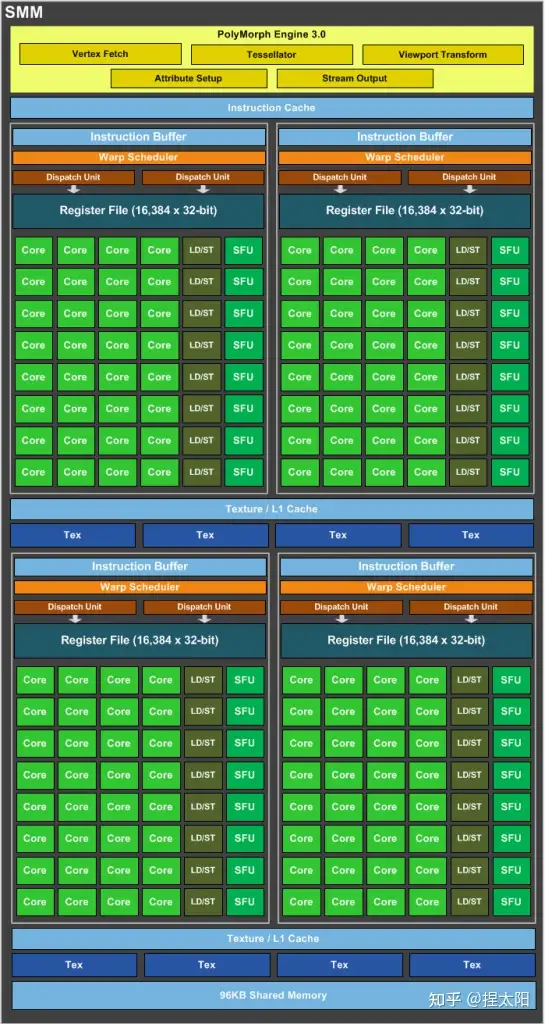
Maxwell¶
- SMM:四个处理块 (processing block),每个有专用的 warp 调度器,包含 32 个 core
pascal¶
NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 Ti Specs | TechPowerUp GPU Database GeForce GTX 1080 Whitepaper
Compute Capability: 6.0(P100), 6.1(GTX 10x、P40、P6、P4), 6.2
Pascal GPUs are composed of different configurations of Graphics Processing Clusters (GPCs), Streaming Multiprocessors (SMs), and memory controllers. The combination of one SM plus one Polymorph Engine is referred to as a TPC.
我找到的 GP104 的图 (6.1)
GP100 是这样的 (6.0)
GP100 Pascal Whitepaper
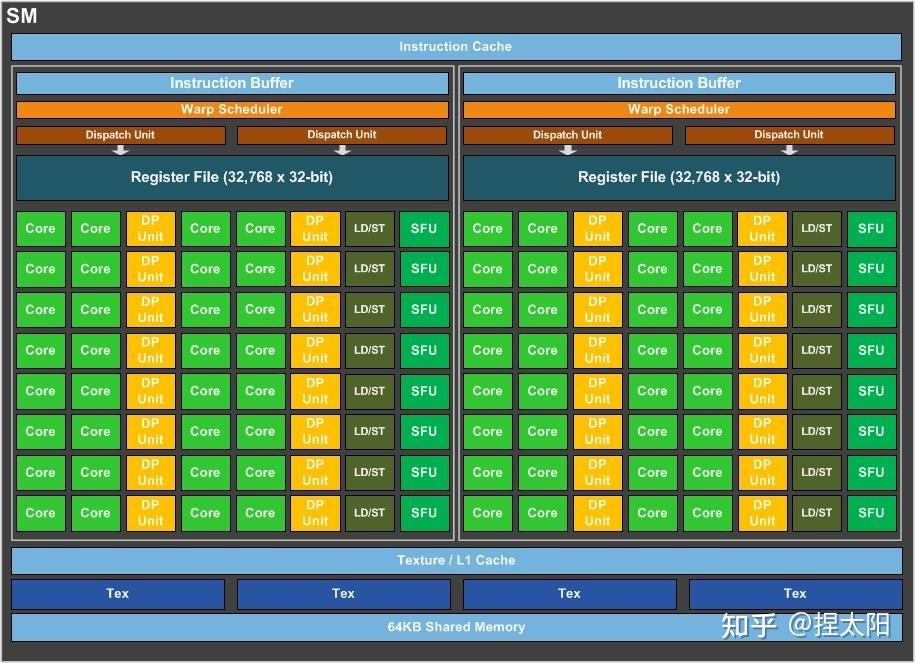
CUDA C++ Programming Guide - 64 (compute capability 6.0) or 128 (6.1 and 6.2) CUDA cores for arithmetic operations, - 16 (6.0) or 32 (6.1 and 6.2) special function units for single-precision floating-point transcendental functions, - 2 (6.0) or 4 (6.1 and 6.2) warp schedulers.
While Fermi and Kepler GPUs featured a 64 KB configurable shared memory and L1 cache that could split the allocation of memory between L1 and shared memory functions depending on workload, beginning with Maxwell, the cache hierarchy was changed. The GP100 SM has its own dedicated pool of shared memory (64 KB/SM) and an L1 cache that can also serve as a texture cache depending on workload. The unified L1/texture cache acts as a coalescing buffer for memory accesses, gathering up the data requested by the threads of a warp prior to delivery of that data to the warp
Pascal architecture comprises two major variants: GP100 and GP104.2 A detailed overview of the major improvements in GP100 and GP104 over earlier NVIDIA architectures are described in a pair of white papers entitled NVIDIA Tesla P100: The Most Advanced Datacenter Accelerator Ever Built for GP100 and NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080: Gaming Perfected for GP104.
Pascal provides improved FP16 support for applications, like deep learning, that are tolerant of low floating-point precision.
GP100 and GP104 provide different FP16 throughputs. GP100, designed with training deep neural networks in mind, provides FP16 throughput up to 2x that of FP32 arithmetic. On GP104, FP16 throughput is lower, 1/64th that of FP32. However, compensating for reduced FP16 throughput, GP104 provides additional high-throughput INT8 support not available in GP100.
Unified L1/Texture Cache¶
Like Maxwell, Pascal combines the functionality of the L1 and texture caches into a unified L1/Texture cache which acts as a coalescing buffer for memory accesses
GP104 默认 global load 不使用 cache。
By default, GP100 caches global loads in the L1/Texture cache. In contrast, GP104 follows Maxwell in caching global loads in L2 only, unless using the LDG read-only data cache mechanism. As with previous architectures, GP104 allows the developer to opt-in to caching all global loads in the unified L1/Texture cache by passing the
-Xptxas -dlcm=caflag tonvccat compile time.
L1 cacheline 使用 32B ?之前 Maxwell bypass L1 的原因是粒度为 128B,没有 sector cache。
Kepler serviced loads at a granularity of 128B when L1 caching of global loads was enabled and 32B otherwise. On Pascal the data access unit is 32B regardless of whether global loads are cached in L1. So it is no longer necessary to turn off L1 caching in order to reduce wasted global memory transactions associated with uncoalesced accesses.
L1/Texture cache which acts as a coalescing buffer for memory accesses, gathering up the data requested by the threads of a warp prior to delivery of that data to the warp.
shared memory¶
Kepler 和 L1 公用,Maxwell 和 Pascal 使用单独的空间。
- GP100 64KB
- GP104 96KB
For Kepler, shared memory and the L1 cache shared the same on-chip storage. Maxwell and Pascal, by contrast, provide dedicated space to the shared memory of each SM, since the functionality of the L1 and texture caches have been merged. This increases the shared memory space available per SM as compared to Kepler: GP100 offers 64 KB shared memory per SM, and GP104 provides 96 KB per SM.
- Algorithms with significant shared memory capacity requirements (e.g., radix sort) see an automatic 33% to 100% boost in capacity per SM on top of the aggregate boost from higher SM count.
- Applications no longer need to select a preference of the L1/shared split for optimal performance
单个线程块最大为 48KB
Thread-blocks remain limited to 48 KB of shared memory. For maximum flexibility, NVIDIA recommends that applications use at most 32 KB of shared memory in any one thread block. This would, for example, allow at least two thread blocks to fit per GP100 SM, or 3 thread blocks per GP104 SM.
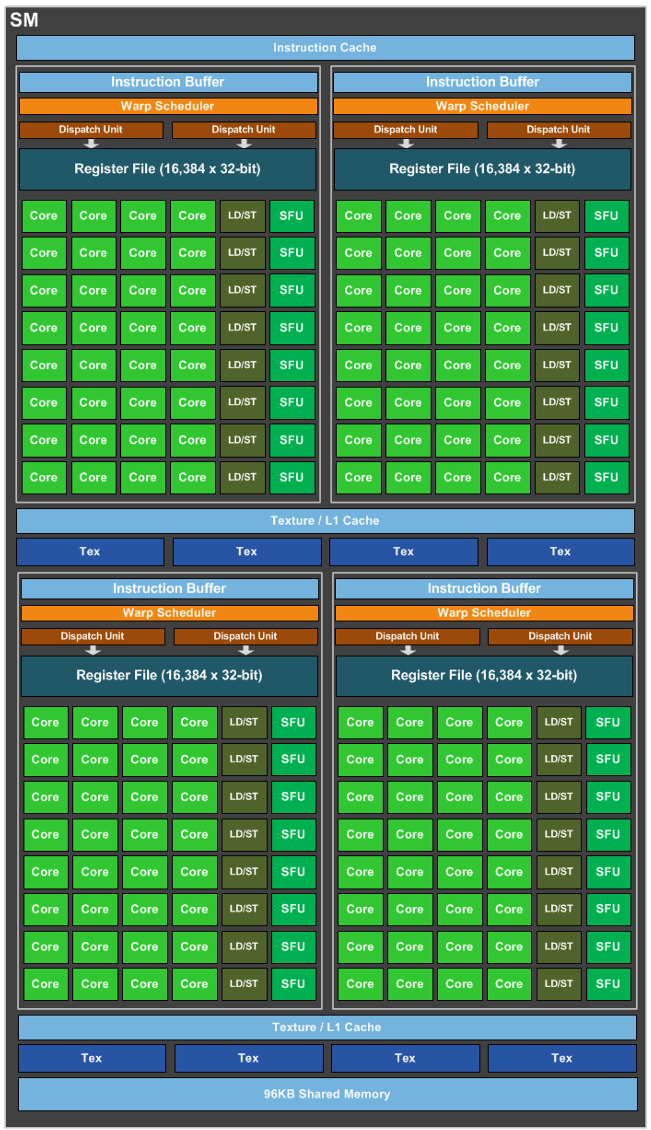
volta¶
Compute Capability: 7.0(TITAN V、V100), 7.2(Xavier)
- SM:4 个 block
- 将一个 CUDA 拆分成 FP32 和 INT32,每个周期可以同时执行浮点和整数。
- 添加 tensor core
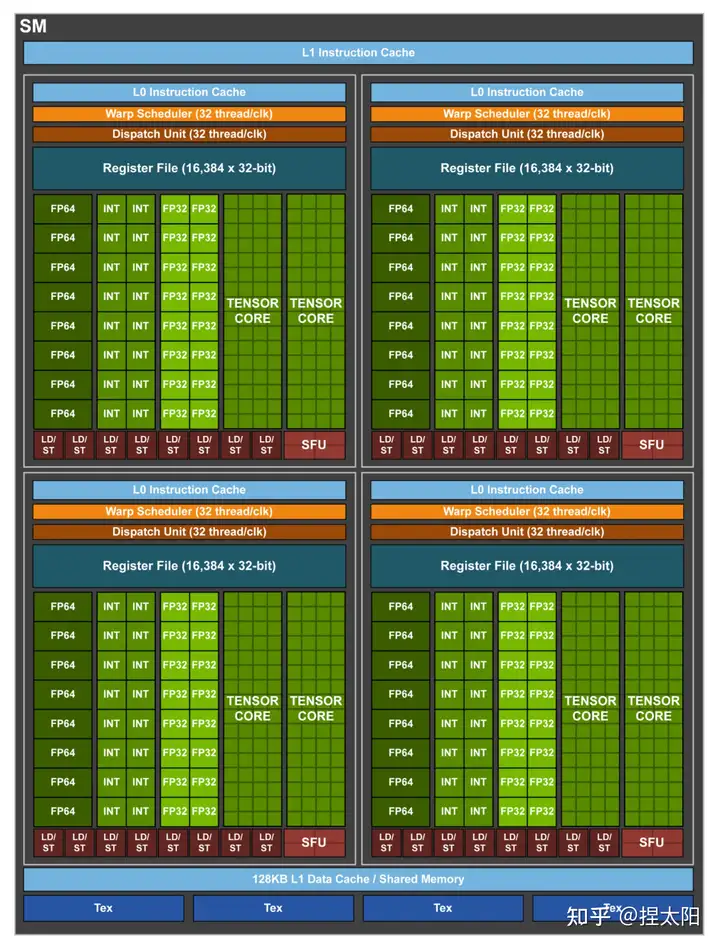
SM¶
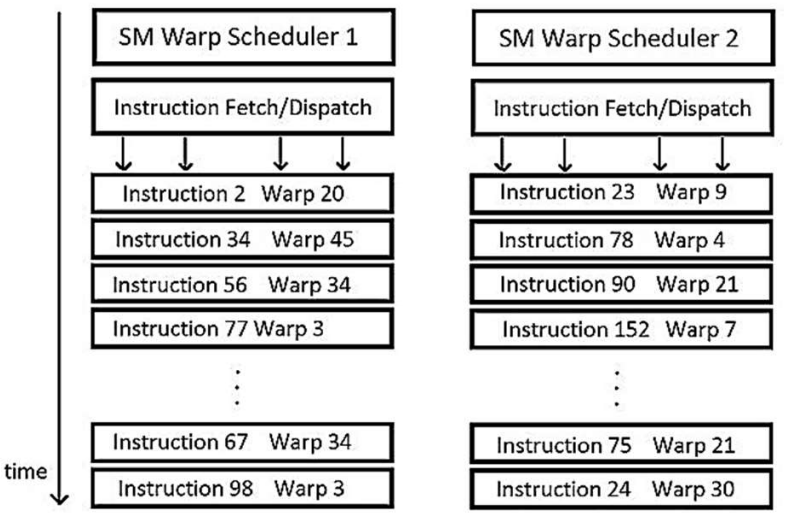
Each Volta SM includes 4 warp-scheduler units. Each scheduler handles a static set of warps and issues to a dedicated set of arithmetic instruction units.
Instructions are performed over two cycles, and the schedulers can issue independent instructions every cycle.
Dependent instruction issue latency for core FMA math operations are reduced to four clock cycles, compared to six cycles on Pascal. As a result, execution latencies of core math operations can be hidden by as few as 4 warps per SM, , assuming 4-way instruction-level parallelism ILP per warp, or by 16 warps per SM without any instuction-level parallelism.
Similar to GP100, the GV100 SM provides 64 FP32 cores and 32 FP64 cores. The GV100 SM additionally includes 64 INT32 cores and 8 mixed-precision Tensor Cores. GV100 provides up to 84 SMs.
dedicated FP32 and INT32 cores. This enables simultaneous execution of FP32 and INT32 operations.
HBM 带宽增大了,SM 数量因此也增加了,来保证 有大量的 reads-in-flight his is accomplished by the large complement of SMs in GV100, which typically boost the number of concurrent threads, and thus the reads-in-flight, compared to previous architectures. Resource-constrained kernels that are limited to low occupancy may benefit from increasing the number of concurrent memory accesses per thread.
unified shared memory/L1/Tex cache¶
carveout 选择
In Volta the L1 cache, texture cache, and shared memory are backed by a combined 128 KB data cache. As in previous architectures, the portion of the cache dedicated to shared memory (known as the carveout) can be selected at runtime using cudaFuncSetAttribute() with the attribute cudaFuncAttributePreferredSharedMemoryCarveout. Volta supports shared memory capacities of 0, 8, 16, 32, 64, or 96 KB per SM.
turing¶
Compute Capability: 7.5(RTX 20x、T4)
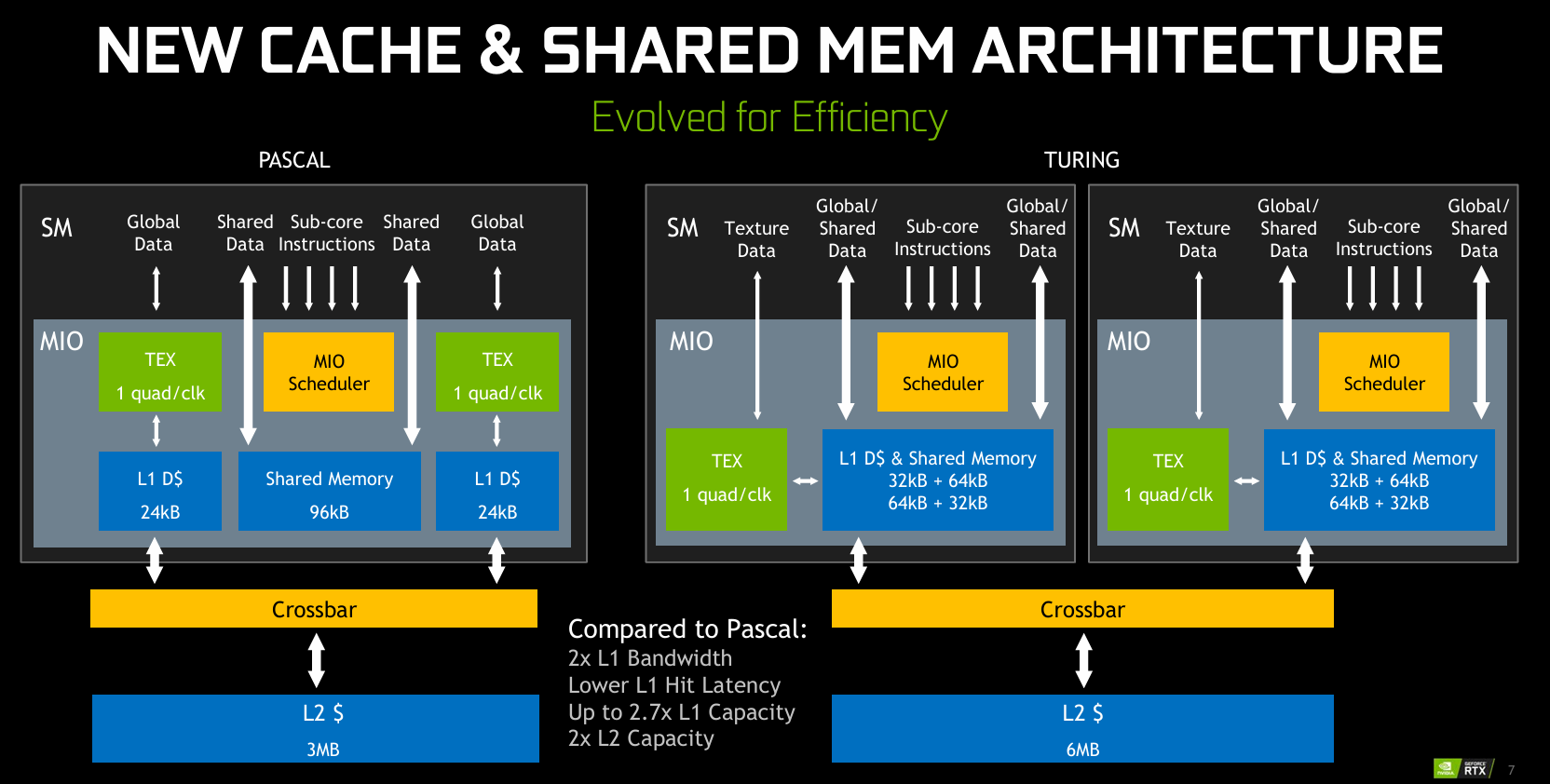
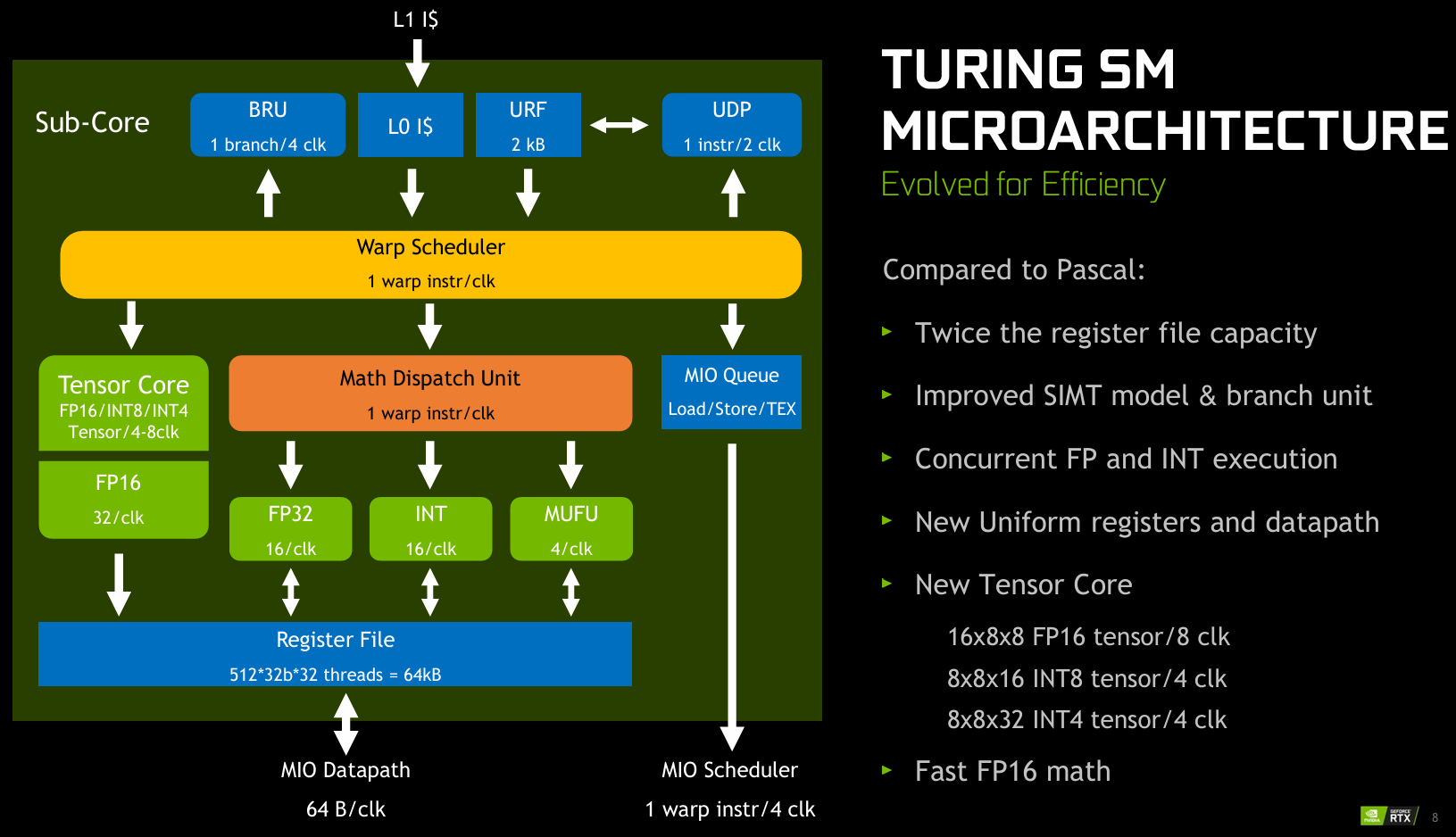
Tensor core 支持整数矩阵乘 Turing adds acceleration for integer matrix multiply operations.
Any binary compiled for Volta will run on Turing, but Volta binaries using Tensor Cores will only be able to reach half of Turing’s Tensor Core peak performance. Recompiling the binary specifically for Turing would allow it to reach the peak performance.
ampere 架构¶
Compute Capability: 8.0(A100、A30), 8.6(RTX 30x、A40、A16、A10、A2), 8.7(Orin)
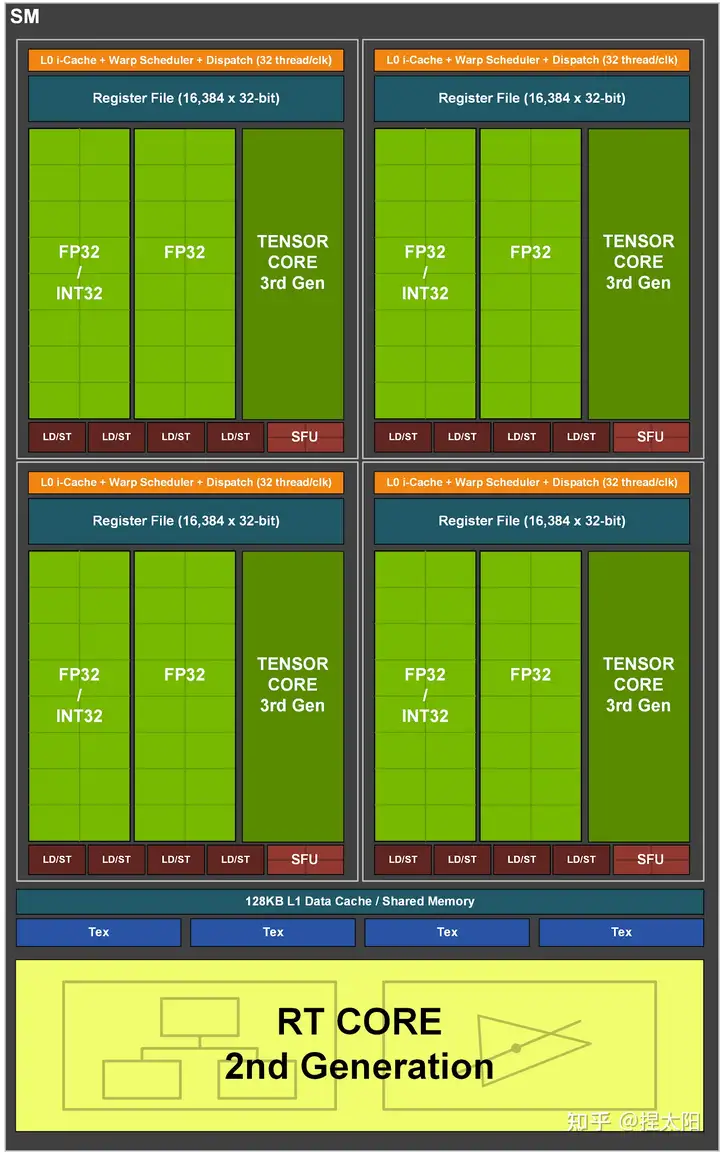
nvidia-ampere-ga-102-gpu-architecture-whitepaper-v2.pdf In the Turing generation, each of the four SM processing blocks (also called partitions) had two primary datapaths, but only one of the two could process FP32 operations. The other datapath was limited to integer operations. GA10x includes FP32 processing on both datapaths, doubling the peak processing rate for FP32 operations
NVIDIA Ampere GPU Architecture Tuning Guide
occupancy¶
- For devices of compute capability 8.0 (i.e., A100 GPUs) shared memory capacity per SM is 164 KB, a 71% increase compared to V100’s capacity of 96 KB. For GPUs with compute capability 8.6, shared memory capacity per SM is 100 KB.
async data copy from global memory to shared memory
- avoid using extra registers
- bypass the L1 cache.
第三代 tensor core¶
- Support for FP64 Tensor Core, using new DMMA instructions.
- Support for Bfloat16 Tensor Core, through HMMA instructions. BFloat16 format is especially effective for DL training scenarios. Bfloat16 provides 8-bit exponent i.e., same range as FP32, 7-bit mantissa and 1 sign-bit.
- Support for TF32 Tensor Core, through HMMA instructions. TF32 is a new 19-bit Tensor Core format that can be easily integrated into programs for more accurate DL training than 16-bit HMMA formats. TF32 provides 8-bit exponent, 10-bit mantissa and 1 sign-bit.
- Support for bitwise
ANDalong with bitwiseXORwhich was introduced in Turing, through BMMA instructions.
Unified L1¶
The NVIDIA A100 GPU based on compute capability 8.0 increases the maximum capacity of the combined L1 cache, texture cache and shared memory to 192 KB, 50% larger than the L1 cache in NVIDIA V100 GPU. The combined L1 cache capacity for GPUs with compute capability 8.6 is 128 KB.
L2 提升 7 倍 40 MB in Tesla A100, which is 7x larger than Tesla V100.
0, 8, 16, 32, 64, 100, 132 or 164
CUDA 架构¶
参考资料¶
基础¶
In CUDA programming, both CPUs and GPUs are used for computing. Typically, we refer to CPU and GPU system as host and device, respectively. CPUs and GPUs are separated platforms with their own memory space. Typically, we run serial workload on CPU and offload parallel computation to GPUs.
- 三个关键抽象:
- 层次化的线程组
- 共享内存
- 同步
高度可扩展性:
编程模型¶
线程层次¶
kernel
- C++ 函数,被调用时,会被每个 CUDA 线程并行执行。
- 使用__global__声明 kernel 函数
- 使用
<<<...>>>execution configuration syntax,指定使用多少线程执行该 kernel
线程层次
- block:多个线程组成一个线程块。可以是 1,2,3 维的
- 通过
threadIdx索引。如二维 (x, y) 的线程 id 是 (x + y Dx); - 一个块内的线程数是有限制的(当前的 GPU 一般为 1024 个)。因为一个块内的线程会被调度到一个 SM(streaming multiprocessor core) 中,共享该 SM 的片上存储(shared memory)
- 一个块是独立的,可以以任意顺序调度,从而保证了 GPU 的可扩展性(SM 是基本单元,堆 SM)
- shared memory 延迟很低,类似于 L1 cache
- 通过
- grid:多个线程块组成一个 grid。可以是 1,2,3 维的
- 通过
blockIdx索引
- 通过
以下代码声明了 1 个线程块,大小为 NxN。用于将两个 NxN 的矩阵相加。
// Kernel definition
__global__ void MatAdd(float A[N][N], float B[N][N],
float C[N][N])
{
int i = threadIdx.x;
int j = threadIdx.y;
C[i][j] = A[i][j] + B[i][j];
}
int main()
{
...
// Kernel invocation with one block of N * N * 1 threads
int numBlocks = 1;
dim3 threadsPerBlock(N, N);
MatAdd<<<numBlocks, threadsPerBlock>>>(A, B, C);
...
}
以下代码声明了 N/16 x N/16 个线程块,每个大小为 16x16。用于将两个 NxN 的矩阵相加。
// Kernel definition
__global__ void MatAdd(float A[N][N], float B[N][N],
float C[N][N])
{
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
int j = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
if (i < N && j < N)
C[i][j] = A[i][j] + B[i][j];
}
int main()
{
...
// Kernel invocation
dim3 threadsPerBlock(16, 16);
dim3 numBlocks(N / threadsPerBlock.x, N / threadsPerBlock.y);
MatAdd<<<numBlocks, threadsPerBlock>>>(A, B, C);
...
}
- 在线程块内,线程通过 shared memory 来共享数据。并且通过同步操作来协调内存访问
__syncthreads()用于路障同步
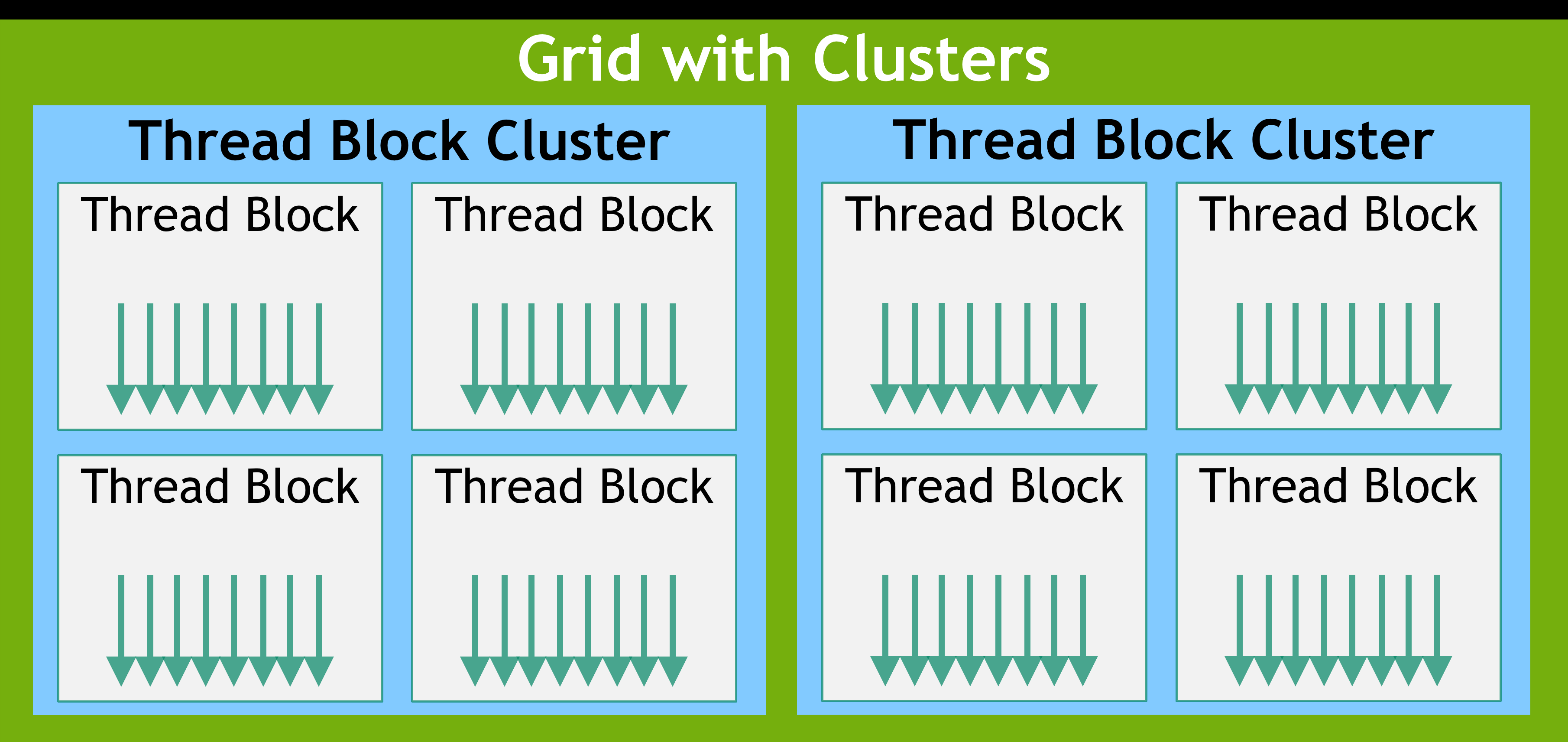
- 线程块蔟:
- CUDA 9.0 中引入的一个可选层次
- 类似于线程块内线程保证在同一个 SM。一个 cluster 内的线程块被调度到同一个 GPU Processing Cluster (GPC)
- 大小一般最大 8 个块
- 支持硬件支持的同步 api。cluster.sync()
Threads within a CTA execute in SIMT (single-instruction, multiple-thread) fashion in groups called warps.
SIMD 和 SIMT 的区别:SIMT 编程时可以控制单个线程。
A key difference is that SIMD vector organizations expose the SIMD width to the software, whereas SIMT instructions specify the execution and branching behavior of a single thread. In contrast with SIMD vector machines, SIMT enables programmers to write thread-level parallel code for independent, scalar threads, as well as data-parallel code for coordinated threads.
SM 能一次能执行多少 block,和每线程 register 数和 block 使用的 shared memory 有关。因为 SM 的寄存器和 shared memory 是给 batch block 所有线程间分配的。如果一个块都执行不了,则 kernel 无法启动。
编程接口¶
- 包含对 C++ 的少量扩展和 rutime 库
C++ 扩展
- 定义 kernel
- 指定线程数
CUDA runtime
- 执行在 host 上
- 分配回收 device 内存
- 在 host 和 device 间传输数据
- 管理多个 device
编译
- 将 device 代码编译成 ptx 或 cubin
- 将 host 代码编译,和 runtime 链接
- runtime 基于底层另一层抽象层,该抽象层再基于 driver API。
兼容性
- cubin 只能在小版本里后向兼容。cubin object generated for compute capability X.y will only execute on devices of compute capability X.z where z≥y.
- PTX 可以后向兼容,但是无法利用新硬件特性。a binary targeting devices of compute capability 7.0 (Volta) compiled from PTX generated for compute capability 6.0 (Pascal) will not make use of Tensor Core instructions, since these were not available on Pascal.
- 后向兼容 (backward):旧编译的可以在新平台上运行
硬件实现¶
https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-c-programming-guide/index.html#hardware-implementation
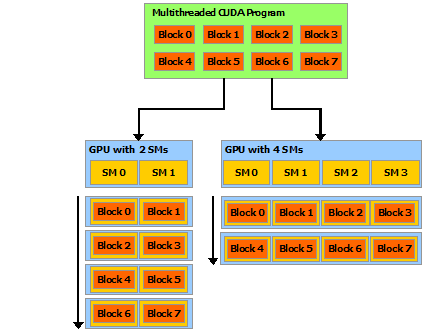
The NVIDIA GPU architecture is built around a scalable array of multithreaded Streaming Multiprocessors (SMs). When a CUDA program on the host CPU invokes a kernel grid, the blocks of the grid are enumerated and distributed to multiprocessors with available execution capacity. The threads of a thread block execute concurrently on one multiprocessor, and multiple thread blocks can execute concurrently on one multiprocessor. As thread blocks terminate, new blocks are launched on the vacated multiprocessors.
- 英伟达 GPU 架构由 SM 数组组成,具有可扩展性。
- 当 host 上的一个 CUDA 程序调用一个 kernel grid 时,grid 中的线程块被分发到有计算能力的 SM 上执行。
- 一个线程块内的线程在一个 multiprocessor 内并发执行,并且多个线程块也可以并发调度到一个 SM 上(当一个线程块终止时,新的块补上) p.s 这里说的是并发,可能需要和并行区分
- SM 被设计来并发执行上百个线程,采用了 SIMT 架构(Single-Instruction, Multiple-Thread)
- 单线程内利用流水线实现 ILP
- 通过同时多线程(simultaneous hardware multithreading)实现线程级并行
- 和 CPU 的 SMT 不同。Unlike CPU cores, they are issued in order and there is no branch prediction or speculative execution.
SIMT¶
自己的理解:CPU 一个核可以并发执行两个线程(超线程技术),而 GPU 一个 SM 可以并发运行成百上千的线程。为了做到这点,采用了 SIMT 技术
- warp
- warp 内的线程执行
- SM 以一个 warp 32 个线程为单位,进行调度。The multiprocessor creates, manages, schedules, and executes threads in groups of 32 parallel threads called warps.
- 每个 warp 的线程从相同的 PC 开始执行。但是它们内部有自己的 PC 可以单独跳转。Individual threads composing a warp start together at the same program address, but they have their own instruction address counter and register state and are therefore free to branch and execute independently.
- SM 将线程块划分为 warp 进行调度。When a multiprocessor is given one or more thread blocks to execute, it partitions them into warps and each warp gets scheduled by a warp scheduler for execution
- 线程块的划分很简单,连续的线程被划分在一起。The way a block is partitioned into warps is always the same; each warp contains threads of consecutive, increasing thread IDs with the first warp containing thread 0.
- warp 中的线程从相同地址开始执行,如果线程因为数据相关的分支造成分叉,warp 执行每一条代码路径,同时禁止非该代码路径上的线程。A warp executes one common instruction at a time. ... If threads of a warp diverge via a data-dependent conditional branch, the warp executes each branch path taken, disabling threads that are not on that path.
- 分叉只发生在 warp 内,不同 warp 是独立的。Branch divergence occurs only within a warp; different warps execute independently regardless of whether they are executing common or disjoint code paths.
- GPU 的 SIMT 和 SIMD 有点类似,都是单条指令处理多个数据。The SIMT architecture is akin to SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) vector organizations in that a single instruction controls multiple processing elements.
- 关键的不同在于,SIMT 既可以实现线程级并行(对于独立的标量线程),又可以实现数据级并行(对于合作线程)。SIMT enables programmers to write thread-level parallel code for independent, scalar threads, as well as data-parallel code for coordinated threads.
- volta 之前的架构,warp 内 32 个线程公用相同的 PC。导致分叉路径上的线程无法相互通信。Prior to NVIDIA Volta, warps used a single program counter shared amongst all 32 threads in the warp together with an active mask specifying the active threads of the warp. As a result, threads from the same warp in divergent regions or different states of execution cannot signal each other or exchange data, and algorithms requiring fine-grained sharing of data guarded by locks or mutexes can easily lead to deadlock, depending on which warp the contending threads come from.
Hardware Multithreading¶
- 执行上下文包含 PC,寄存器。warp 上下文被保存在片上(而不是软件保存),因此 warp 切换没有损失。The execution context (program counters, registers, and so on) for each warp processed by a multiprocessor is maintained on-chip during the entire lifetime of the warp. Therefore, switching from one execution context to another has no cost,
Shared memory or cache ?¶
起初没有 L1/L2 --> 引入 scratch pad --> cache 越来越大
I think it is fair to say that the importance of shared memory in CUDA programming has decreased with the advent of L1/L2 caches of competitive size in GPUs. For use cases requiring peak performance, shared memory can still be important due to the programmer control it provides.
tensor core¶
v100 whitepaper
The Volta tensor cores are accessible and exposed as Warp-Level Matrix Operations in the CUDA 9 C++ API. The API exposes specialized matrix load, matrix multiply and accumulate, and matrix store operations to efficiently use Tensor Cores from a CUDA-C++ program. At the CUDA level, the warp-level interface assumes 16x16 size matrices spanning all 32 threads of the warp. In addition to CUDA-C++ interfaces to program Tensor Cores directly, cuBLAS and cuDNN libraries have been updated to provide new library interfaces to make use of Tensor Cores for deep learning applications and frameworks. NVIDIA has worked with many popular deep learning frameworks such as Caffe2 and MXNet to enable use of Tensor Cores for deep learning research on Volta GPU based systems. NVIDIA is working to add support for Tensor Cores in other frameworks as well.
aaa¶
unified memory¶
Beyond GPU Memory Limits with Unified Memory on Pascal | NVIDIA Technical Blog
背景
- 两个 memory space
- 应用不能 oversubscribing GPU 内存,开发者必须手动管理 active working set
- 双、四和八 GPU 系统在工作站和大型超级计算机中变得越来越普遍,在 CPU 和 GPU 之间手动管理数据很困难
- 某些应用程序基本无法手动管理:光线追踪引擎发射的光线可以根据材料表面向任何方向反弹。如果场景不适合 GPU 内存,光线可能很容易击中不可用的表面,必须从 CPU 内存中获取。在这种情况下,如果没有真正的 GPU 页面故障功能,几乎不可能计算出哪些页面应该在什么时间迁移到 GPU 内存。
特点
- 统一内存于 2014 年随 CUDA 6 和 Kepler 架构一起推出。这种相对较新的编程模型允许 GPU 应用程序在 CPU 函数和 GPU 内核中使用单个指针,从而大大简化了内存管理。
- CUDA 8 和 Pascal 架构通过添加 49 位虚拟寻址和按需页面迁移 (on-demand page migration),显著改进了统一内存功能。
- 简单来说就是实现了 page fault。The Page Migration engine allows GPU threads to fault on non-resident memory accesses so the system can migrate pages from anywhere in the system to the GPUs memory on-demand for efficient processing.
- CUDA 8 还添加了通过向运行时提供提示来优化数据局部性的新方法,因此仍然可以完全控制数据迁移。
memory space¶
local global co
CUDA and Applications to Task-based Programming¶
CUDA and Applications to Task-based Programming (cuda-tutorial.github.io)
part1 编程模型¶
- CPU latency-oritened
- large L1
- ILP
- GPU througput-oriented
- vast number of parallel processors
- over-subscribe, latency hiding
- CUDA: Compute Unified Device Architecture
- driver API: cu
- runtime API: cuda
- device runtime API
- driver API is superset of runtime API, provide a few additional advanced features.
有用的参考资料¶
- Essential reading
- CUDA Programming Guide
- CUDA API Reference Manual
- PTX Instruction Set Architecture
- Building executables
- CUDA Compiler Driver NVCC
- Debugging & profiling
- CUDA-MEMCHECK
- Nsight Documentatio
__global__: be invoked straight from the host and must not have a return value other than void.
- Launch configuration, parameters (built-in types, structs, pointers)
__device__: be called from functions already running on the device, such as kernels or other device functions.__host__: 修饰运行在 CPU 上的函数 - 同时指定 device 和 host,可以用于实现一些架构无关的函数
同步
- kernel call 对于 host 是异步的,然而 kernel call 之间默认不是异步的,因此 cuda 默认假设连续的 kernel calls or copy instructions are dependent on previous events, and order them accordingly。
- 同步命令
- cudaDeviceSynchronize() to synchronize CPU and GPU
- cudaEventSynchronize() to synchronize up to certain event
运行¶
使用 warp 的原因,为了利用 SIMD 单元 For the sake of exploiting SIMD hardware units, threads will always execute in groups of 32, regardless of the block size being used.
volta 改进了 warp(单独 PC) Before Volta: not understanding warps may crash your application After Volta: not caring about warps may make your application slower
SM
- cuda core: synonym for the units that perform integer or floating-point arithmetic
- LD/ST
- SFU
- tensor core
warp 执行模型¶
block queue
- the blocks that make up a grid are committed to the GPU in a block queue.
- GPU will then proceed to process the blocks in parallel. The degree of parallelisms depends on the hardware being used but is transparent to the developer: block 被完全分配给一个 SM 一个 SM 可以运行多个 block
- 如何考虑 shared memory 的共享? SM 选择 ready 的 warp 执行,
- SM 的 warp 越多,并行效率越高?The more warps an SM has to choose from, the higher the chances are that it can hide latency by switching to different warps.
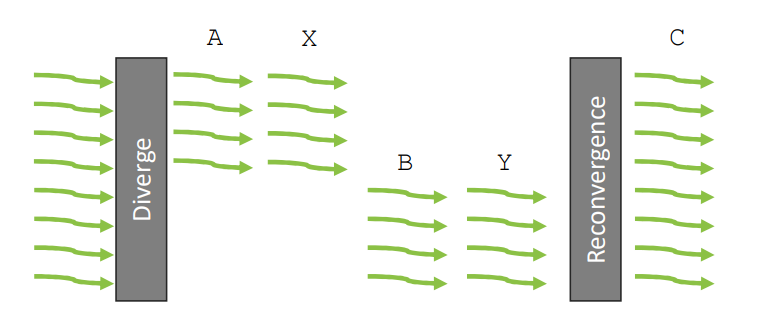
warp 作为一个整体执行,warp 中的线程同时执行下一条指令
- 线程可以分叉(diverged)
SIMT 正式解释:既可以看作单独的线程,又可以像 SIMD 一样高效(只要不分叉)
- 每个线程有一个 active flag 控制是否参与 warp 内的计算 This architecture design, which enables threads to behave like individual entities, while still enabling the exploitation of efficient SIMD operations when threads are not diverged is described by the term “same-instruction-multiple-threads”, or SIMT for short.
CUDA thread execution model¶
- Legacy Thread Scheduling
- Independent Thread Scheduling (ITS)
legacy(“lockstep”)
- warp 只有一个 PC 值
- warp 中的所有线程在每个时钟周期都执行相同的指令
- inactive will not execute current instruction
- diverges 时,先执行一部分,再执行另一部分
- 在 warp 切换前,会尝试达到合并点。Diverged threads will try to reach convergence point before switching
- 位于分叉的两部分的线程,不能实现一些同步算法,容易造成死锁
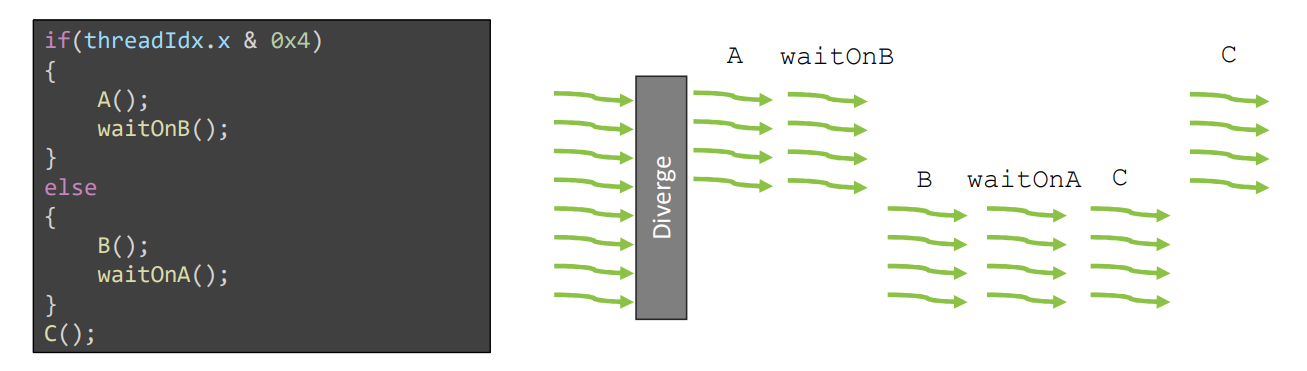
ITS(Independent Thread Scheduling)
- Two registers reserved, each thread gets its own program counter
- 线程的执行仍然发生在 warp,It is not possible for threads in a warp to perform different instructions in the same cycle
- 也就是说仍然无法一起执行 A 和 B
- ITS provides a “progress guarantee”: eventually, over a number of cycles, all individual program counters that the threads in a warp maintain will be visited
- they are free to stay diverged until the program finishes. The GPU will try to make threads reconverge at opportune times,
- 通过显示的同步指令保证所有线程执行相同的指令。synchronization command
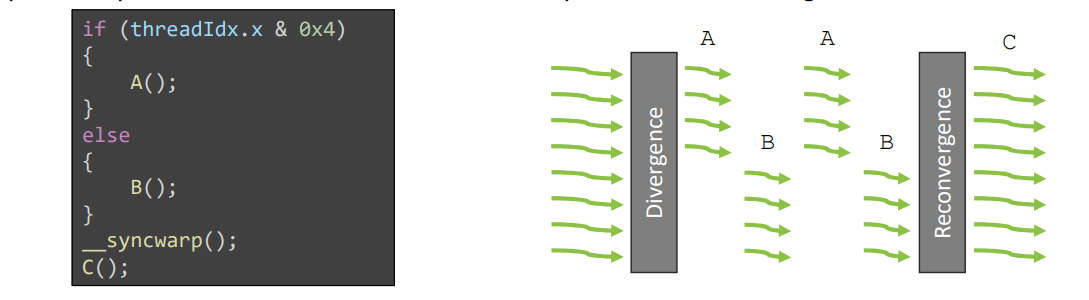
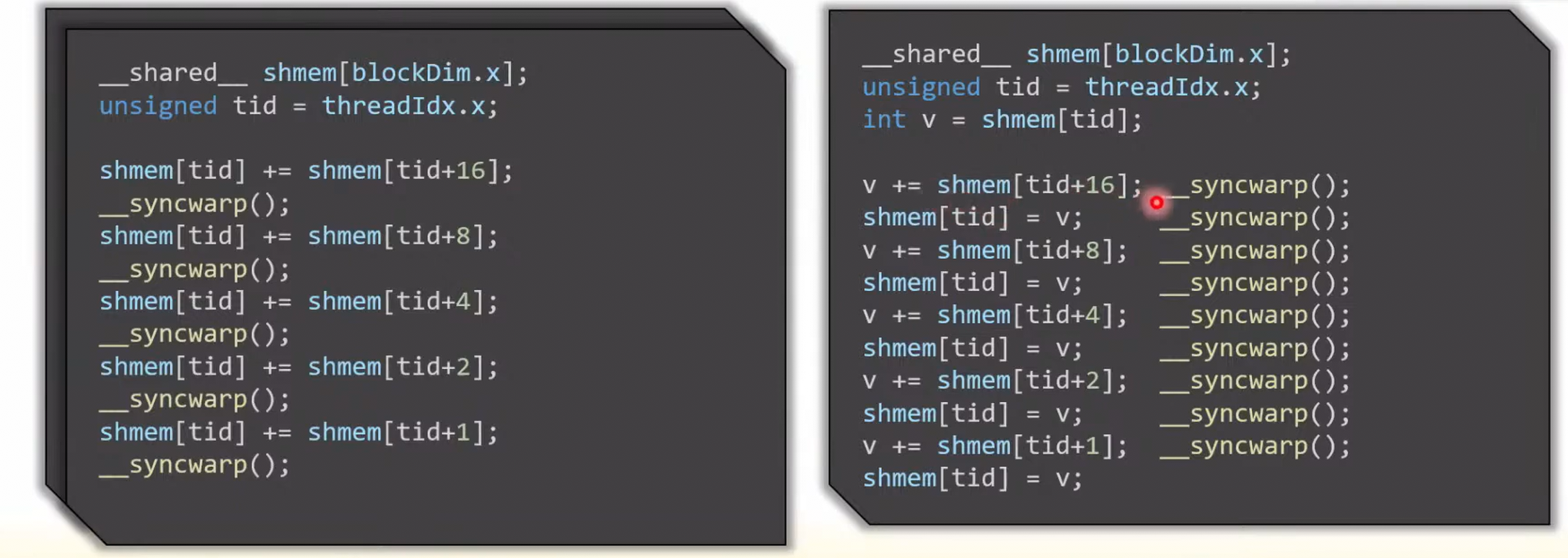
__syncwarp
- 只对 volta 之后的架构有意义(支持 ITS)
- 可以通过 mask 只同步一个子集线程。32bit integer, where each bit indicates whether or not a thread with the corresponding ID should participate in the synchronization.
__syncthreads()
- All active threads must reach the same instruction in the program
this_grid().sync() can busy-wait to synchronize entire kernel
正常来说,CUDA 编程范式(programming paradigm)包含 grid-block-thread 三层。但是由于线程是按照 warp 调度的,因此正确利用 warp 的性质可以极大提高性能。
Warp-level primitives are instructions where threads in one warp exploit the fact that they run together to quickly share information
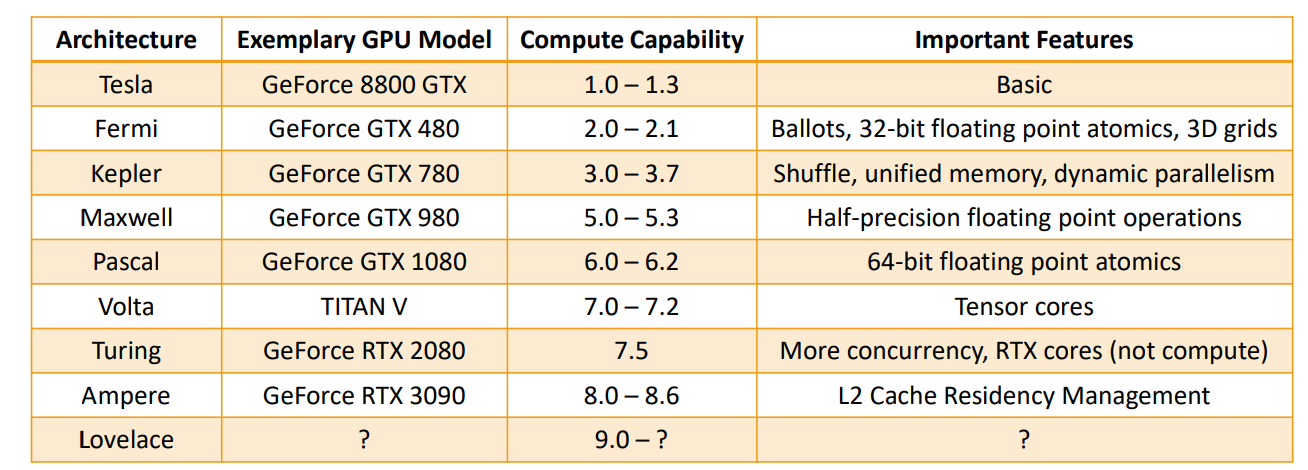
reduce 优化例子¶
1 reduce global
- N 次 read, store global memory
- read 会经过 cache,那么其它 sm 读取的时候会反复出现 invalid cache 的情况吗?

2 reduce shared
- 使用 shared 快速的内存累加
- 将操作 global memory 降低为 N/256
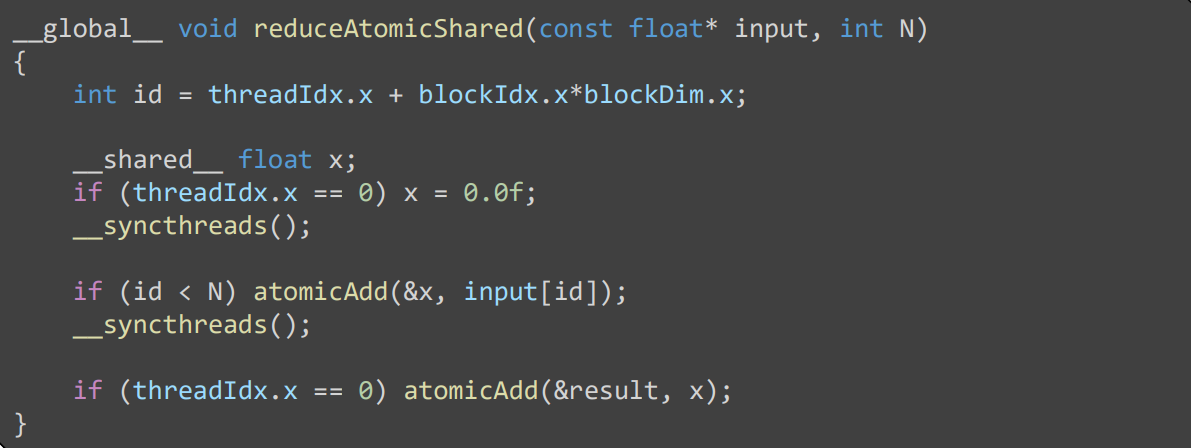
前面的均是顺序规约,可以使用 subliner 的算法
3
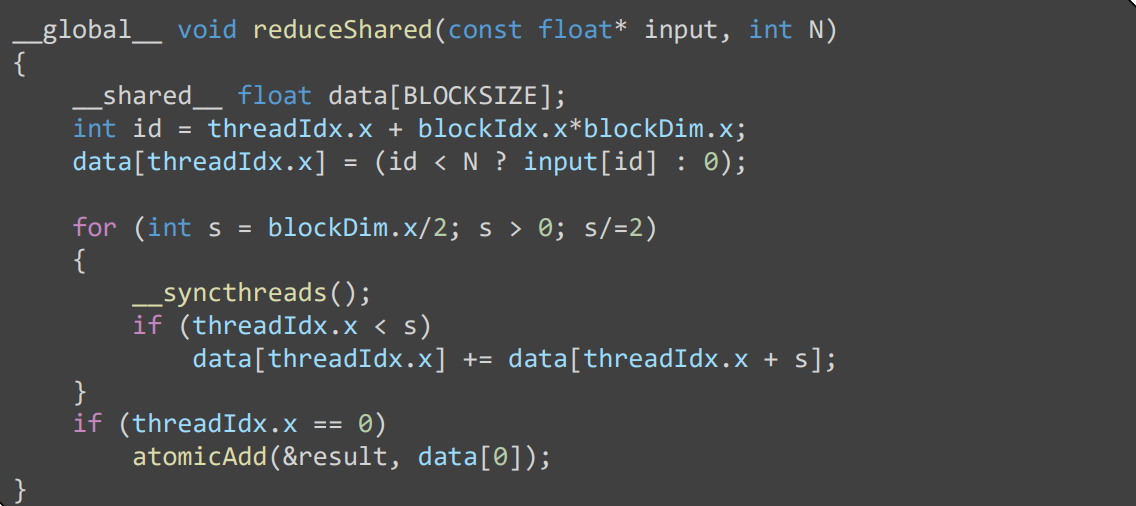
4
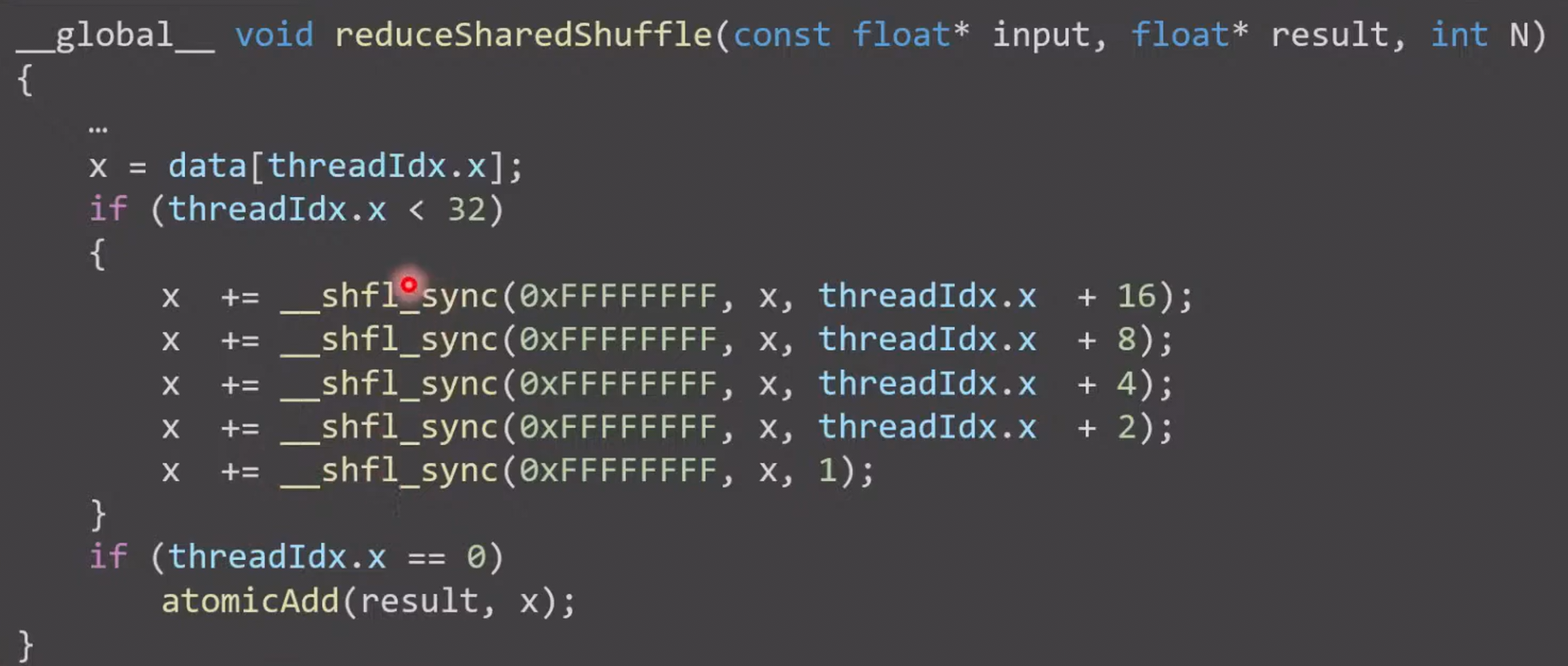
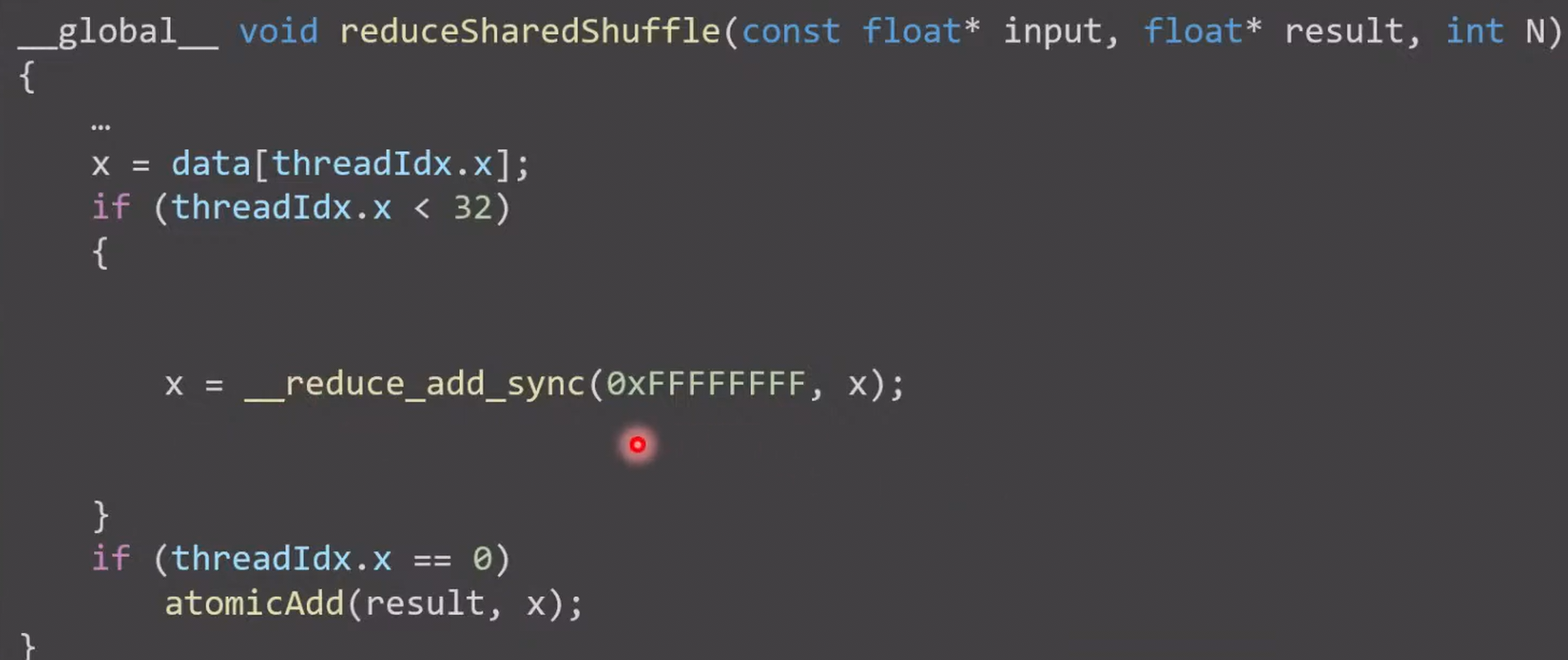
- 使用寄存器做最后 32 个数据的规约
- In the first iteration, each thread in the warp will try to read the value of the thread with an ID that is 16 higher than its own.
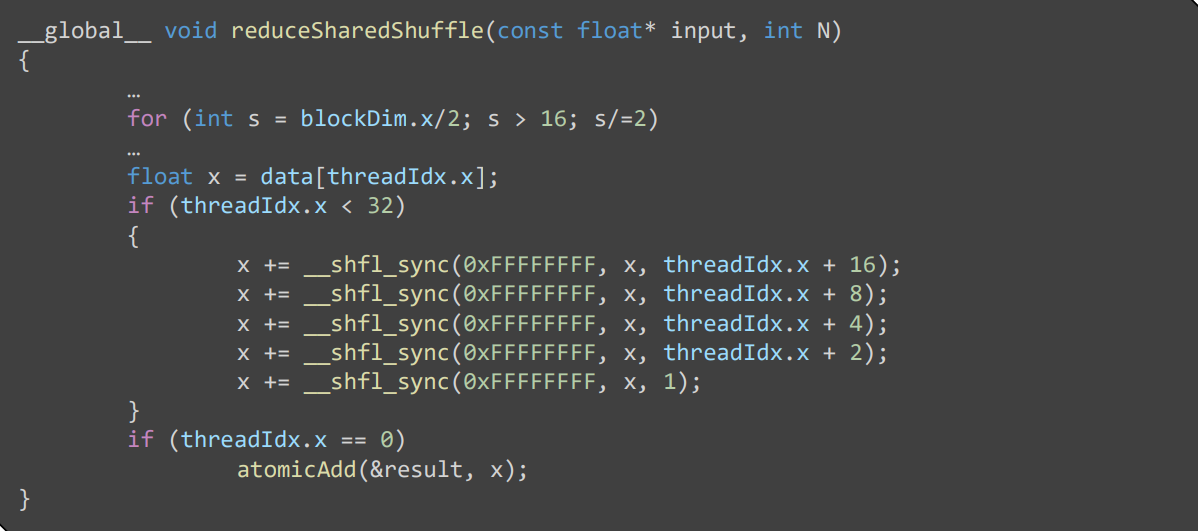
- In the first iteration, each thread in the warp will try to read the value of the thread with an ID that is 16 higher than its own.
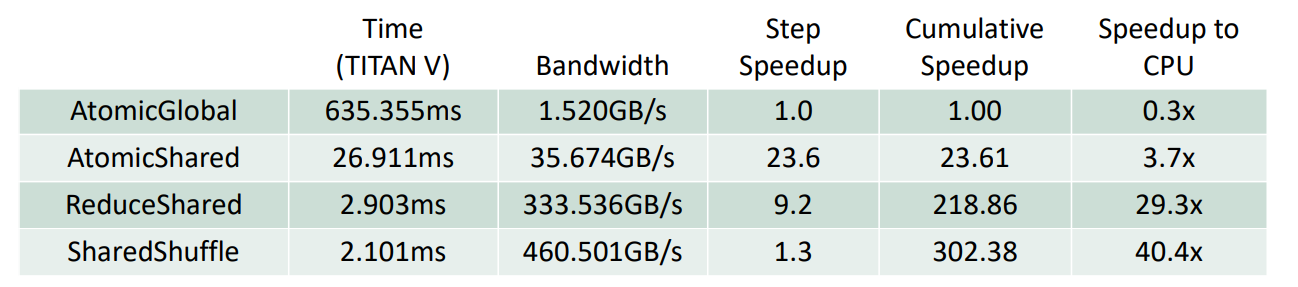
stream¶
CUDA will assume that kernels depend on each other unless indicated otherwise.
stream
- stream 之间没有依赖
- launch 时通过第 4 个参数指定 stream,默认为“null”stream
- 调用 CUDA runtime API 时,传递 stream 参数。如 cudaMemcpyAsync
debug¶
nsight vscode plugin: Nsight Visual Studio Code Edition
- Overview reveals warps, active and valid masks of individual threads
cuda-memcheck suit
cuda-memcheck –-tool <tool> <application>
• memcheck: memory errors (access violations, leaks, API errors)
• synccheck: misuse of synchronization (invalid masks, conditions)
• racecheck: data races (read-after-write, write-after-read hazards)
• initcheck: evaluation of uninitialized values (global memory only
- CUB/Thrust: additional primitives and functions similar to standard library
- Algorithms: e.g., prefix sum, scan, sort • Data structures and containers: e.g., vectors
- cuBLAS: basic linear algebra subprograms (BLAS) on top of CUDA
- cuFFT: efficient implementation of discrete fourier transform on the GPU
- cuSparse: algorithms and optimizations for working with sparse matrices
- TensorRT: interface to learning and inference capabilities with tensor cores
- CUTLASS: provides a range of templates for tensor core matrix computations
Compiler Explorer (godbolt.org)
- 支持 cuda c++
- 支持 PTX 和 SASS
part 2 hardware 实现¶
编译¶
host 和 device 部分分开编译
host code
- takes care of loading matching GPU binary stored in .exe
- translate kernel
<<<…>>>(…)syntax into API call
“Fat Binary” can contain both
- PTX for various compute capabilities
- allows the binary to target unknown architecture
- precompiled machine code for specific GPU architectures
- optimal performance on certain known devices
PTX
- 生成机器码
- ptxas
- driver at runtime(JIT)
SASS(Shader Assembly?)
- nvdisasm.exe
- 没有文档
硬件设计¶
- GPU 设计成最大化吞吐量
- 不等待长延迟操作,而是切换到其它任务
设计对比
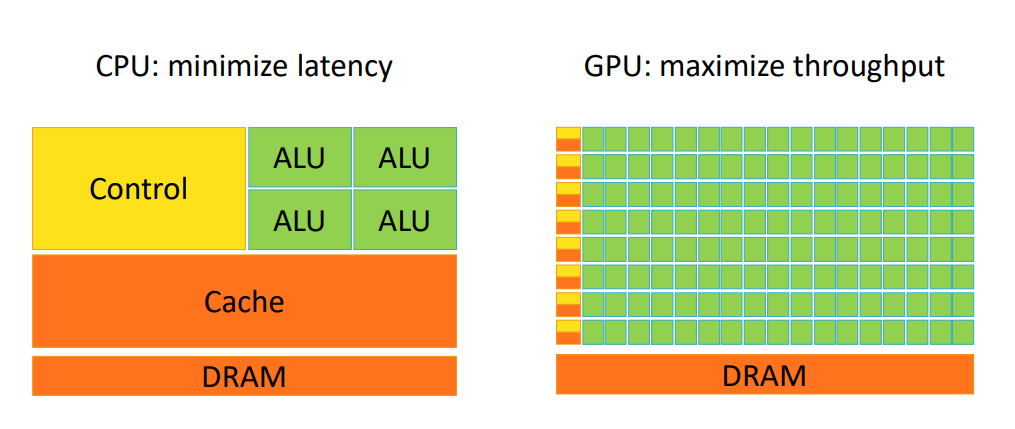
CPU:优化 single flow 速度
- larget cache
- complex control logic for out-of-order execution
GPU
- simple control
- many core
- large register
- keep context resident on chip, enable rapidly switch
- rely on SIMD
- Each control logic is associated with multiple arithmetic logic units (ALUs), allowing for the parallel execution of multiple control flows
two-level hierarchy that consists of groups of groups of SIMD cores.
- GPU
- SM
- warp scheduler
- register file
- a set of ALU: INT32, FP32, FP64, Tensor Core, LD/ST unit, SFU
- shared memory
- L1 cache
- warp scheduler
- SM
each warp scheduler is assigned a set of warps to execute
- The execution context of all threads that are part of each warp is kept locally in the register file associated with the warp scheduler responsible for the warp
Whenever it could issue a new instruction (e.g., each clock cycle unless all of the necessary resources are occupied), the warp scheduler will pick the next instruction from one of its warps that are ready to run (i.e., not waiting on the result of a previous operation) and schedule it to the appropriate hardware unit.
- 单发射?
- 看来时 SIMD 形式发射
warp 切换隐藏延迟,warp scheduler 从 reay 的 warp 中选择一个执行其指令(假设 SIMD),遇到访存指令,如果下一条指令依赖访存指令数据,则将 warp 置于 suspend queue。然后切换到另一个 ready warp。因此只要一直能切换 warp,访存延迟就可以被隐藏。
So far, we have simply assumed that all threads within a warp always need to run the same instruction next, allowing us to execute all threads of a warp in parallel in SIMD fashion
warp 实现¶
对于 diverge 的处理,属于猜测
predication
- 指令通过 1bit prediction,来决定是否执行
- 程序一直执行下一条指令,有一些分支的 EXIT 指令在 pred 的作用下生效,避免执行其它分支的代码
- 缺点:
- However, control flow is forced to pass over all instructions on both sides of every branch
- 有些 branch,没有线程执行。仍然要遍历所有 path,导致 significant overhead especially as branches are nested more and more deeply
- However, control flow is forced to pass over all instructions on both sides of every branch
- 对于更复杂的控制,比如函数调用,无法实现
先执行一部分,再执行另一部分,最后合并。
- 如何决定执行顺序呢?
- 顺序执行,保证能遍历到所有分支
- 更复杂的情况?
- 嵌套循环
- 必须遍历完所有分支(即使没有线程执行)
- 使用 CSR 栈

CSR(Call, Return, Synchronization)
- warp 调度器维护一个栈:mask(32bit),合并点
- 遇到分支指令时,将一个分支的 mask 和合并点 push 到 stack,然后执行另一个分支 (~mask),结束时 sync,从 stack 中 pop 恢复
CUDA and Application to Task-Based Programming (part 1) | Eurographics'2021 Tutorial (youtube.com)
- 2:17:30,解释 CSR
ITS
- Instead of just scheduling warps as a whole, the warp scheduler can switch between active branches of warps. While execution of divergent branches still has to be serialized, it can be interleaved
- 调度的单位从 warp 变为了 branch
- 消除了 intra-warp synchronization 的限制
- 延迟隐藏:larger set of potential work to choose from

memory 层次¶
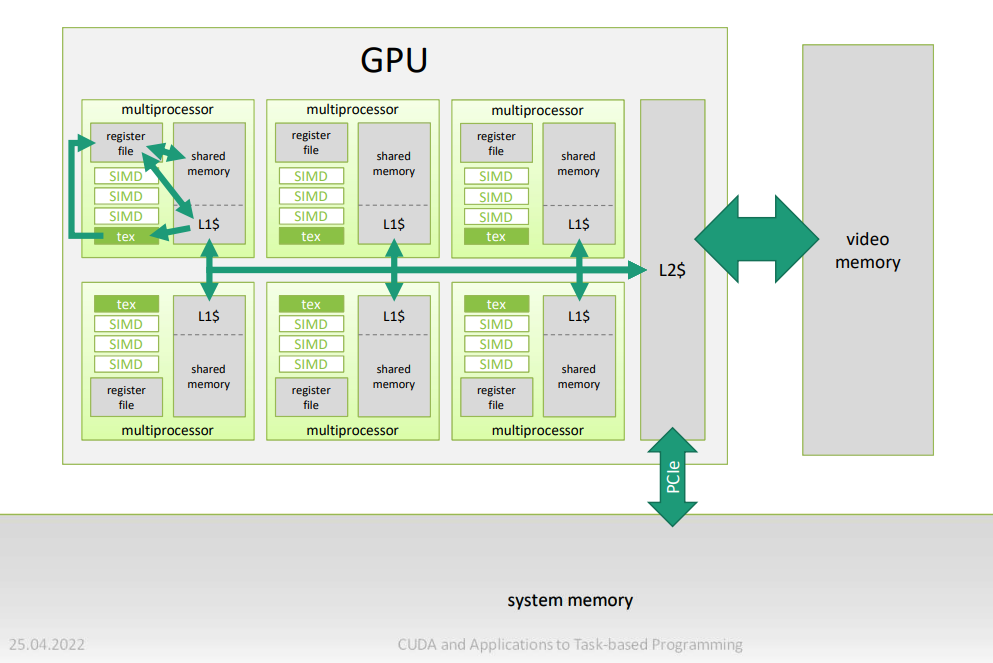
In CUDA, these hardware resources are exposed in the form of a number of memory spaces, each with different properties designed for different kinds of access patterns.
global¶
- 一般的数据存储
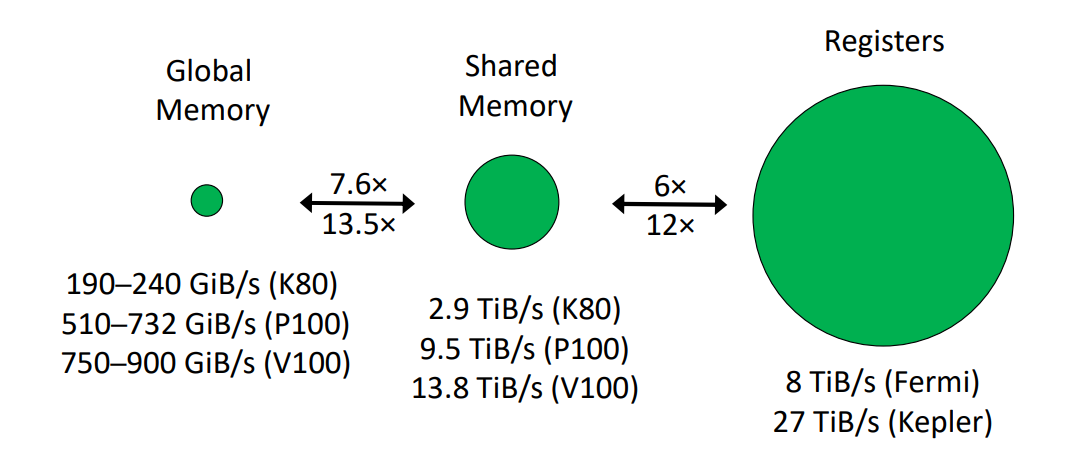
- 很慢:bandwidth: ≈ 300–700 GiB/s (GDDR5/6 vs HMB2) • non-cached coalesced access: 375 cycles • L2 cached access: 190 cycles • L1 caches access: 30 cycles
- cache 设计:
- 不是为了利用时间复用,而是 smooth-out access patterns
- 64 B L1$, 37 B L2$ per thread
- 不要像 CPU 一样分块,而是使用 shared memory
- L1 写直达,L2 写回
- 不是为了利用时间复用,而是 smooth-out access patterns
- try to get coalescing per warp
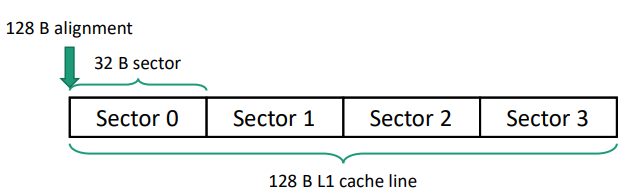
粒度实验
- 性能随着访问的 cacheline 数目增长而线性降低
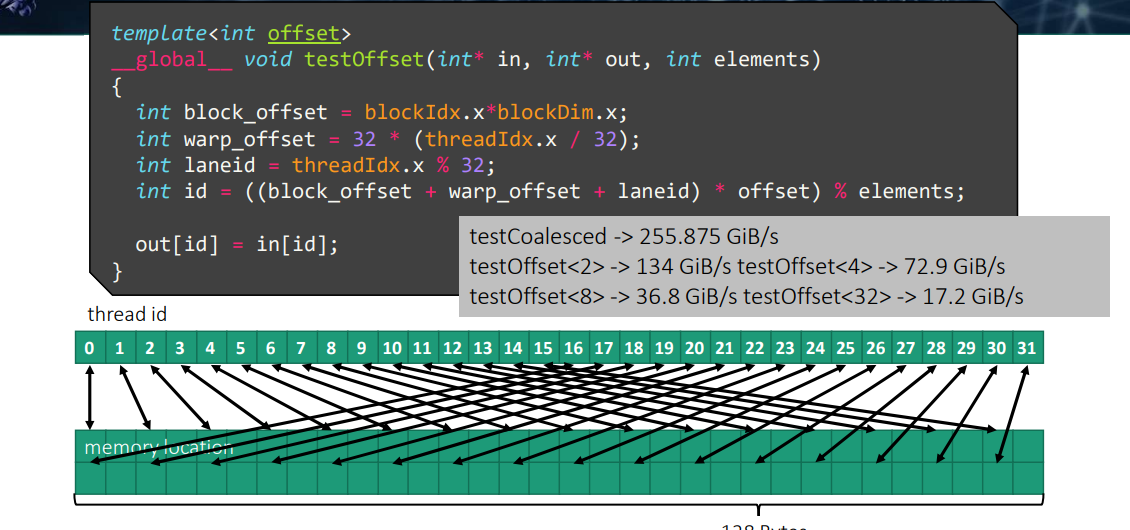
vector load/store
- 计算地址没办法延迟隐藏,因为访存操作对其结果有依赖
__restrict:This instructs the compiler to assume that the input and output will never point to overlapping memory regions.
- As a result, the compiler can potentially, e.g., fetch input data through faster non-coherent caches.
128bit 宽(16B)
const¶
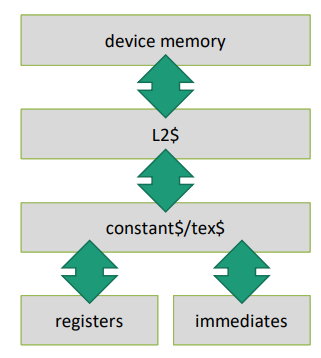
- cached
- const cache,过去叫 texture cache
- read only, uniform
- e.g.: coefficients, used to pass kernel parameters
- broadcasting
- all thread read same value
- otherwise diverged, slowdown
- limited to 64 KiB
- As long as access happens uniformly, constant memory can provide very low access latencies.
- For divergent access patterns, normal global memory can typically provide better access latencies due to its different cache design (as long as the access hits the cache).
tex¶
optimized for 2D spatial access.
- optimal for neither row-wise nor column-wise access, it can handle both with similar efficiency.
prior to Volta • Textures tend to perform at least as good, sometimes better • put less stress on L2 cache • L1 cache free for other tasks
now • advanced Unified Cache (L1 + Tex) • Textures still perform best for spatially local access pattern • but can also be slower if access pattern and cache hits favor linear memory
shared memory¶
crossbar
- 32bit bank
- simultaneous to distinct bank
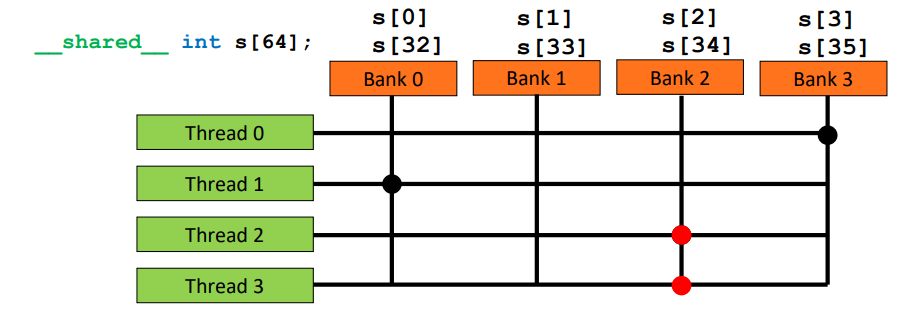
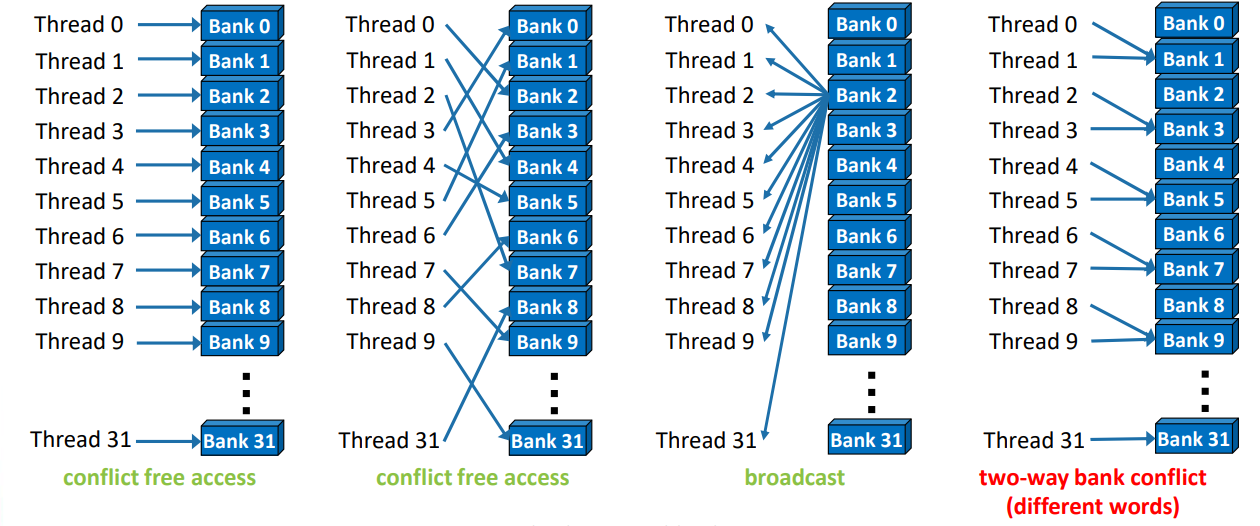
shared memory
- 32 bank, consecutive 4-byte elements map to one bank
- Each memory bank can serve 4-byte loads and stores from and to the addresses it’s responsible for.
- 同一时间不能有多个 thread 访问同一个 bank
- N-way bank conflict
- 特殊情况,访问相同地址,可以广播
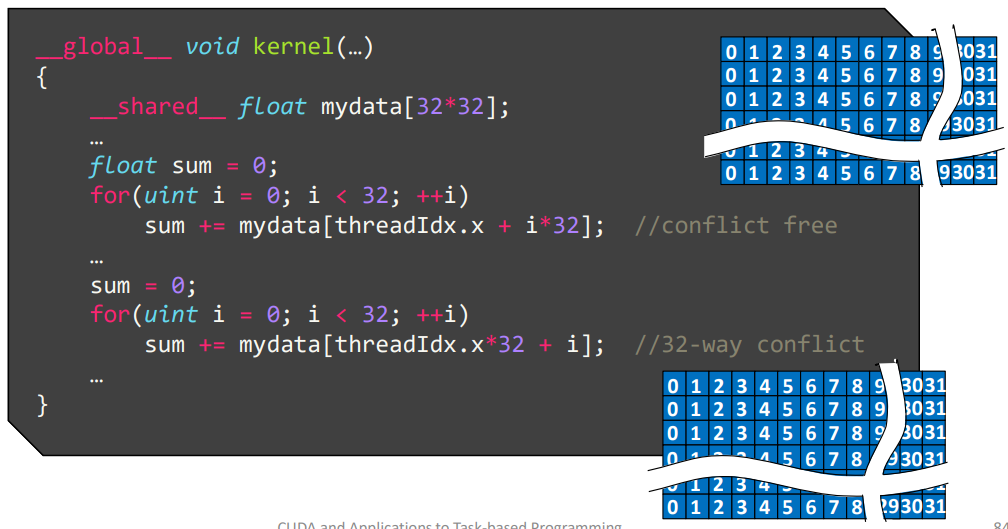
32x32 的 matrix,对行列分别求和,使用 32 个线程并行
- 每列元素位于相同 bank,因此行求和时,每个线程刚好访问相同 bank,导致冲突
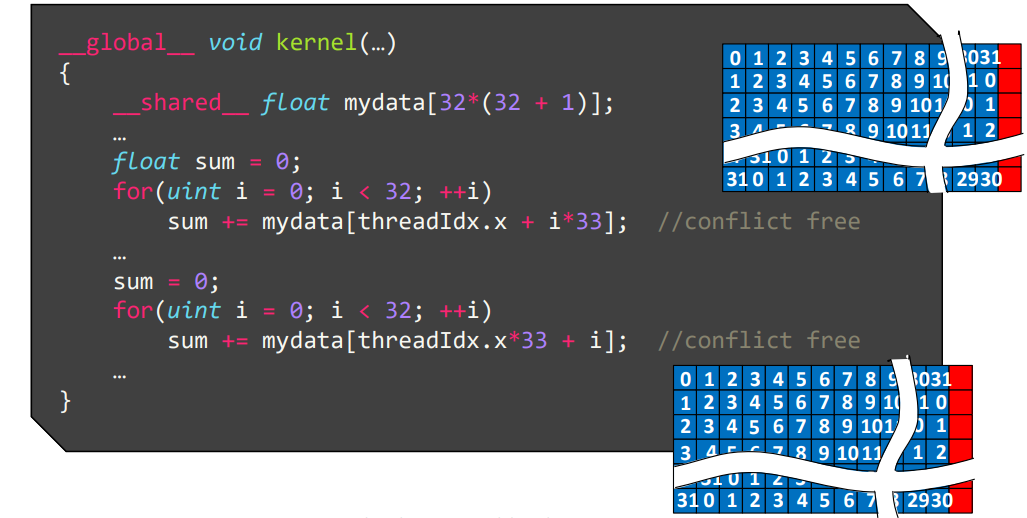
trick
- 添加一个 dummy colum 后,每行每列元素均位于不同 bank
作用
- inter-thread communication:block 内的一个共享变量
- reduce global memory access -> manual cache
- 先把数据从 global load 到 shared memory 再处理
- adjust global memory access pattern
- indexed access
- 普通变量数组,会 spill 到 local memory 中
- combine costly operations
part 3¶
managed memory¶
static 分配:device
dynamic 分配 (cpu 代码执行分配):cudaMalloc
movement
- cudaMemcpy, cudaMemcpyToSymbol, cudaMemcpyFromSymbol
managed mem
- static:
__managed__ - dynamic:
cudaMallocManaged
在 CC(compute capac)6.0 之前,data migration 是粗粒度的,不支持 CPU 和 GPU concurrent access。 6.0 之后,引入细粒度的 page fault system,页为粒度,性能大幅提高
- concurrent access 仍然不能保证。
ITS¶
legacy
- 所有线程位于同一个 PC。需要执行完一个分支后再执行另一个(因为只有一个 PC,线程无法单独记录自己的位置)
- 执行一个分支时,将另一个分支压入栈中即可(dfs?)该分支执行结束时通过 sync 语句弹栈,回到合并点。
its
- 可以用于实现锁
- 只保证 resident warp 是可以执行完的
- thread will wait forever if their progress depends on non-redident warp
- 一个 SM 能同时执行的 warp 是有限的,如果 warp 太多,会放在 buffer 里,仍有可能导致死锁?
- 需要显示同步 warp
later warp primitve
 reduce(>8.0)
reduce(>8.0)
tensor core¶
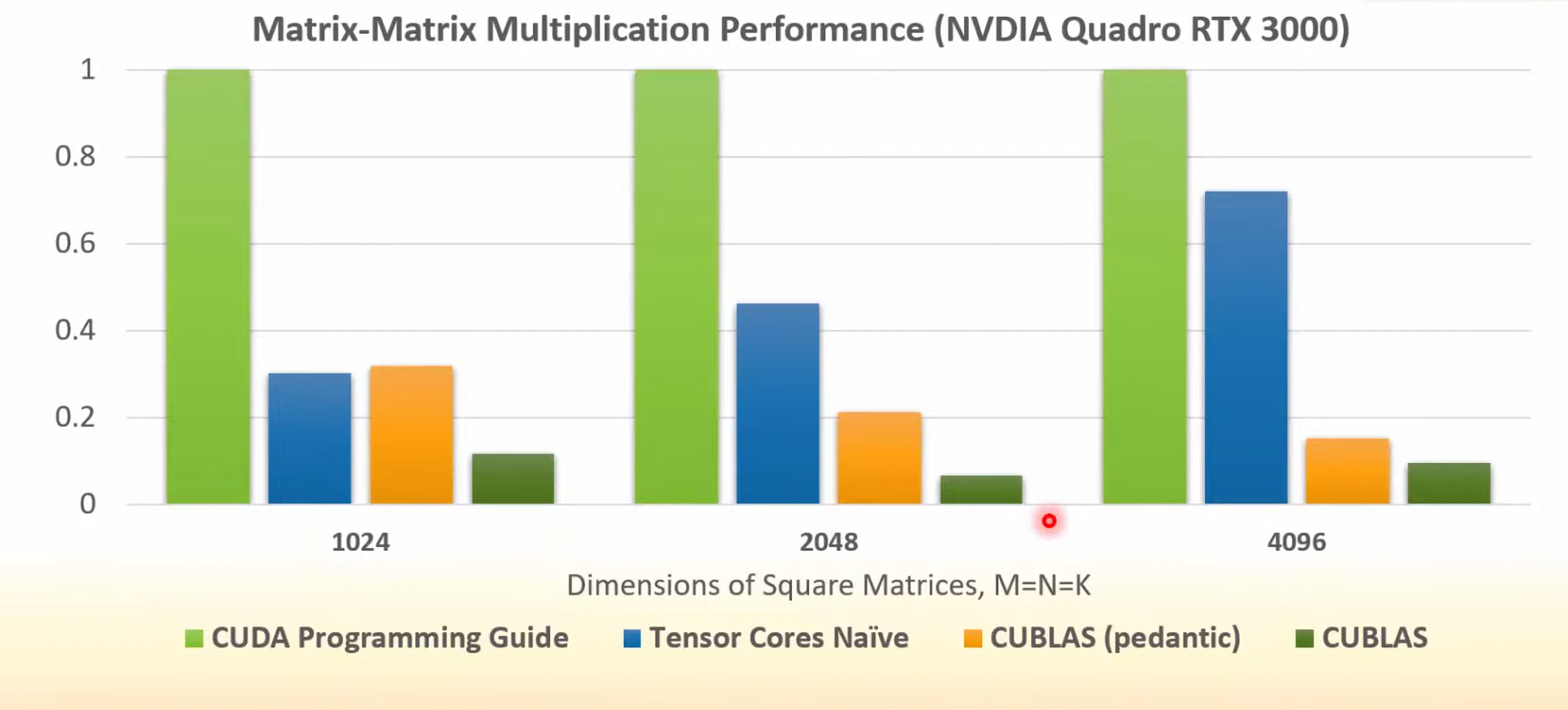
- cublas 以后默认会尽可能使用 tensor core,除非定义 CUDA_PREDANTIC_MATH
- baseline 是使用 tiling, shared memroy,可以看到 cublas 非常重要。
- 但是分析模型如何分析闭源的 SASS 可执行文件呢?
- 但是分析模型如何分析闭源的 SASS 可执行文件呢?