openwrt 编译
openwrt 编译
Openwrt 编译¶
说明¶
自己编译优点¶
- 固件体积减小(需要安装的 package 被压缩到镜像中)
- 可以定制一些需要的选项(busybox 可以选择 zsh)
- 下次刷机,可以不用进行软件安装,配置
The main advantage of building your own firmware is that it compresses the files, so that you will have room for much more stuff. It is particularly noticeable on routers with 16 MB flash RAM or less. It also lets you change some options that can only be changed at build time, for instance the features included in BusyBox and the block size of SquashFS. Larger block size will give better compression, but may also slow down the loading of files. (ref: [OpenWrt Wiki] Quick image building guide)
Openwrt Build System 特点¶
- 不用配置编译链
While it is possible to manually create your toolchain, and then build OpenWrt with it, this is difficult and error-prone. The OpenWrt build system takes a different approach to building a firmware: it downloads, patches and compiles everything from scratch, including the cross compiler. Or to put it in simpler terms, OpenWrt's build system doesn't contain any executables or even sources. It is an automated system for downloading the sources, patching them to work with the given platform and compiling them correctly for the platform. What this means is that just by changing the template, you can change any step in the process. And of course the side benefit of this is that builds are automated, which saves time and guarantees the same result every time. For example if a new kernel is released, a simple change to one of the Makefiles will download the latest kernel, patch it to run on the requested platform and produce a new firmware image. There's no work to be done trying to track down an unmodified copy of the existing kernel to see what changes had been made - the patches are already provided and the process ends up almost completely transparent. This doesn't just apply to the kernel, but to anything included with OpenWrt - it's this strategy that allows OpenWrt to stay on the bleeding edge with the latest compilers, kernels and applications. (ref: [OpenWrt Wiki] Build system essentials)
- 编译出来的 toolchain 位置
staging_dir/toolchain…is a mini Linux root with its ownbin/,lib/, etc that contains the cross C compiler used to build the rest of the firmware. You can actually use that to compile simple C programs outside of OpenWRT that can be loaded onto the firmware. The C compiler might be something like:staging_dir/toolchain-mips_34kc_gcc-4.8-linaro_uClibc-0.9.33.2/bin/mips-openwrt-linux-uclibc-gcc. You can see the version of the CPU, the C library and gcc encoded into it; this allows multiple targets to be built in the same area concurrently.
openwrt git 分支¶
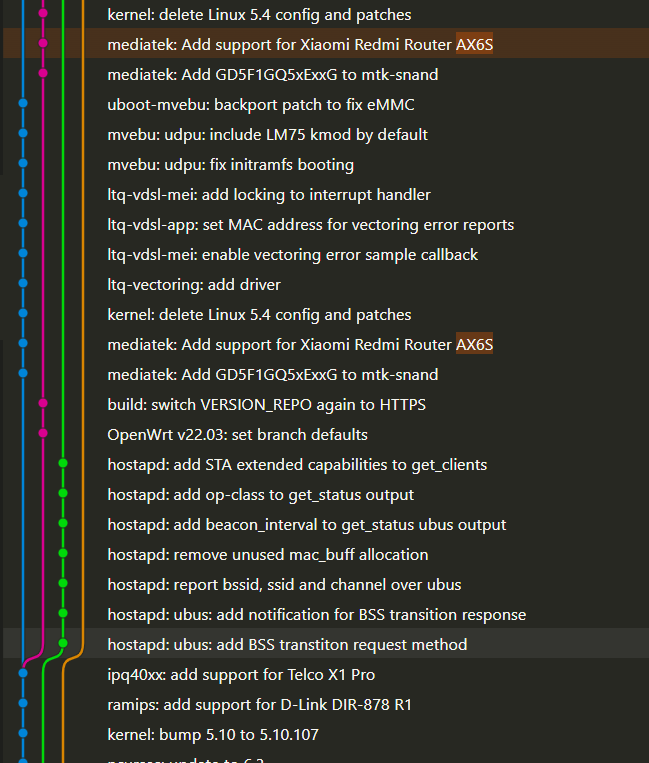
图中蓝色为 master 分支,绿色为 21.02 稳定版分支,橙色为 LEDE19.07 分支,而粉色的为新的 22.03 测试版分支。可以看到 AX6S 最早在 master 分支中得到支持,然后不久便在 22.03 中得到了添加。
- 好奇为何不使用 merge
21.02 稳定版分支,当初也是从 master 分支中分离出来的
immortalwrt¶
- immortalwrt/immortalwrt: An opensource OpenWrt variant for mainland China users. (github.com) 有以下这些分支。开发流程为将官方分支合并到自己的分支。但是 21.02 稳定版仍然没有 AX6S 的支持,网上看到的是 18.06-k5.4 分支的
- AX6S 闭源无线驱动 Openwrt 刷机教程/固件下载 - 小米无线路由器以及小米无线相关的设备 - 恩山无线论坛 (right.com.cn)
* openwrt-21.02
remotes/origin/HEAD -> origin/openwrt-21.02
remotes/origin/master
remotes/origin/openwrt-18.06
remotes/origin/openwrt-18.06-k5.4
remotes/origin/openwrt-21.02
编译命令¶
依赖¶
根据[OpenWrt Wiki] Build system setup 安装对应
编译¶
- 参考:
-
命令汇总
# Download and update the sources git clone https://git.openwrt.org/openwrt/openwrt.git cd openwrt git pull # Select a specific code revision git branch -a git tag git checkout v21.02.1 # Update the feeds ./scripts/feeds update -a ./scripts/feeds install -a # Configure the firmware image and the kernel make menuconfig #make kernel_menuconfig #download all dependency source files before final make, enables multi-core compilation make download # Build the firmware image #make (or make world) #when faild, V=s show all command executed #make V=s make -j $(nproc) 2>&1 | teemake.log
-
Cleaning Up
make clean #deletes contents of the directories /bin and /build_dir. make clean does not remove the toolchain, it also avoids cleaning architectures/targets other than the one you have selected in your .config make dirclean #deletes contents of the directories /bin and /build_dir and additionally /staging_dir and /toolchain (=the cross-compile tools) and /logs. 'Dirclean' is your basic "Full clean" operation. make distclean #nukes everything you have compiled or configured and also deletes all downloaded feeds contents and package sources. #clean small part make target/linux/clean #Clean linux objects make package/base-files/clean #Clean package base-files objects make package/luci/clean #Clean luci
编译配置¶
menuconfig¶
- Target System(MediaTek Ralink MIPS)
- Subtarget(MT7621 based boards)
- Target Profile(Xiaomi Redmi Router AC2100)
- Target Images
- 取消勾选 ramdisk,否者会生成
openwrt-ramips-mt7621-xiaomi_mi-router-4a-gigabit-initramfs-kernel.bin - 勾选 squashfs,可以调节 block size(默认 256B),越大的块压缩率更好,但读取速度更慢(可能影响重启速度?)
- 取消勾选 ramdisk,否者会生成
- Build the Openwrt SDK:一个小的 buildroot,用于测试自己的 package
- Package the Openwrt-based Toolchain:交叉编译链
- Base system
- 使用 Openclash 需要取消勾选 dnsmasq(已经勾选 dnsmasq-full)
- 中文乱码:make menuconfig->Base System->busybox->Customize busybox option->Settings->support unicode 选项(位于结尾)勾上后,勾上选项 Check $LANG environment variable
- Administration
- htop
- Development
- gcc, gdb 等工具
- Fonts
- DejaVu 字体
- Kernel modules
- Other modules: kmod-mtd-rw:开启 uboot 等 flash 分区写权限
- USB support:
kmod-usb-core kmod-usb-storage kmod-usb-uhci kmod-usb2 kmod-usb3 - Video support: kmod-video-core kmod-video-uvc
- Languages
- python:requests, lxml
- Luci
- Collections
- Luci:否则没有图形界面
- Module
- luci-compat:据说是必要的
- Application
- adblock
- ddns
- Openclash(需要自己添加)
- qos
- samba4: usb(需要 usb 挂载东西的话)
- upnp
- wireguard
- wol
- Collections
- Network
- Files Transfer: curl
- VPN: zerotier
- immortalwrt 需要开启: odhcp6c, odhcpd-ipv6only,否则 ipv6 无法使用
- WirelessPAD:
- wpad-openssl:最完整
- wpad-mesh-openssl
- wpad-basic-openssl
- Utilities
- Editors:vim-full(只能选一个)
- Shells:bash, zsh
usb¶
webcam¶
#kmod > video support
kmod-video-core kmod-video-uvc
#Multimedia
mjpg-streamer
input-uvc
output-rtsp
www-simple
#luci
luci-app-mjpg-streamer
#utils(optional)
uvcdynctrl
opkg 安装其它软件¶
必备
有用
mesh¶
immortalwrt¶
interface wan6 显示不支持的协议,需要额外安装以下软件,并 restart network
闭源驱动¶
看到很多非 openwrt 官方固件都提到了闭源驱动因此了解了一波 大概就是 MTK 有 mt76 无线的驱动代码,但是 openwrt 内使用的是自己开发的驱动。 Mt76 driver - replacement [for test] - For Developers - OpenWrt Forum openwrt/feeds/mtk-openwrt-feeds - Gitiles (mediatek.com)
记录¶
无 5Ghz 无线¶
刚开始编译了 rm2100,make clean 后,编译了 r3g。结果发现一切都好,就是没有 5Ghz 无线。而使用官方版本是有的。 尝试 make dirclean 后 (full clean),重新编译,问题解决。
发现在不同设备上都遇到过这个问题,暂不清楚是哪一步导致的
测速速度慢¶
测速上传下载都是 300 左右 尝试保存配置后,在系统中 reset,然后重新加载配置。
- reset 后,速度很快,基本上上传可以到 600-700,下载 900-1000
- 重新加载配置后,速度依旧很快