iptables
iptables
iptables is a command line utility for configuring Linux kernel firewall implemented within the Netfilter project.
- iptables 是 linux 上的防火墙软件
- 有一些工具作为 iptables 的前端,命令更加简单或者有 GUI(如 ufw 和 gufw)
- Note: iptables is a legacy framework, nftables aims to provide a modern replacement including a compatibility layer.
原理¶
Flow chart¶
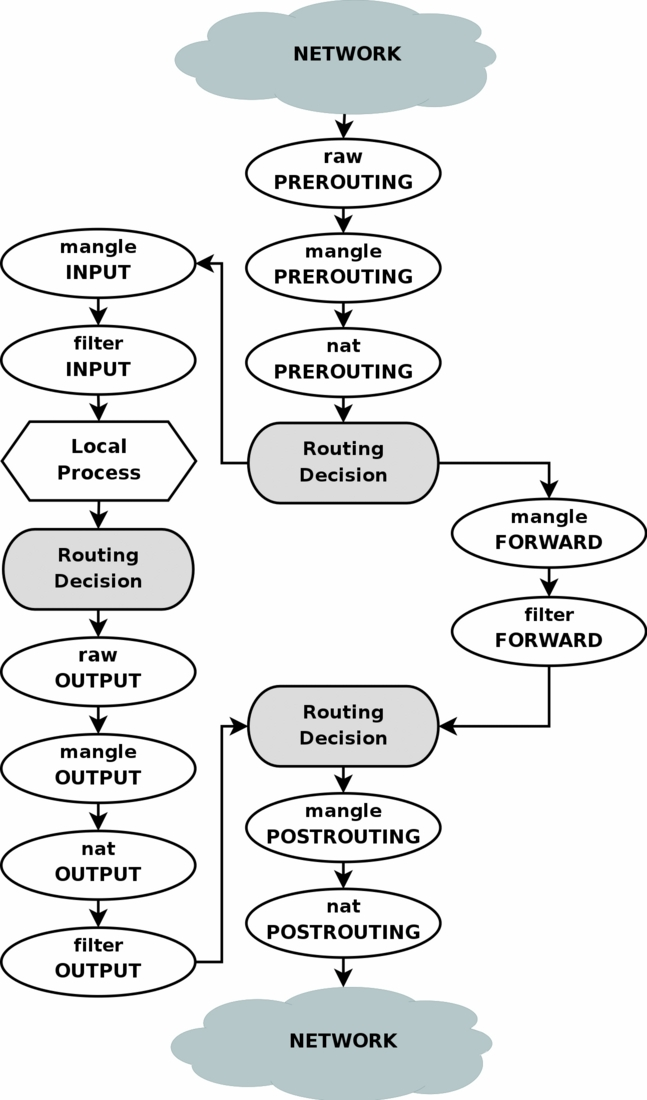
当一个网络接口上接受到一个包后,内核会对其进行一系列处理。
When a packet first enters the firewall, it hits the hardware and then gets passed on to the proper device driver in the kernel. Then the packet starts to go through a series of steps in the kernel, before it is either sent to the correct application (locally), or forwarded to another host - or whatever happens to it.
 )
)
- 每一个 IP 包,无论来自哪一个网络接口 (network interface),都会按照该流图处理
- 大致分为 3 种情况
- 包的目的是本机的某个进程:PREROUTING --> INPUT --> Local Process
- 如果本地进程产生一个包,也需要一系列处理将其发送到某个接口上:OUTPUT --> POSTROUTING
- 如果包的目的地址不是本机,则需要进行转发:PREROUTING --> FORWARD --> POSTROUTING
Tables¶
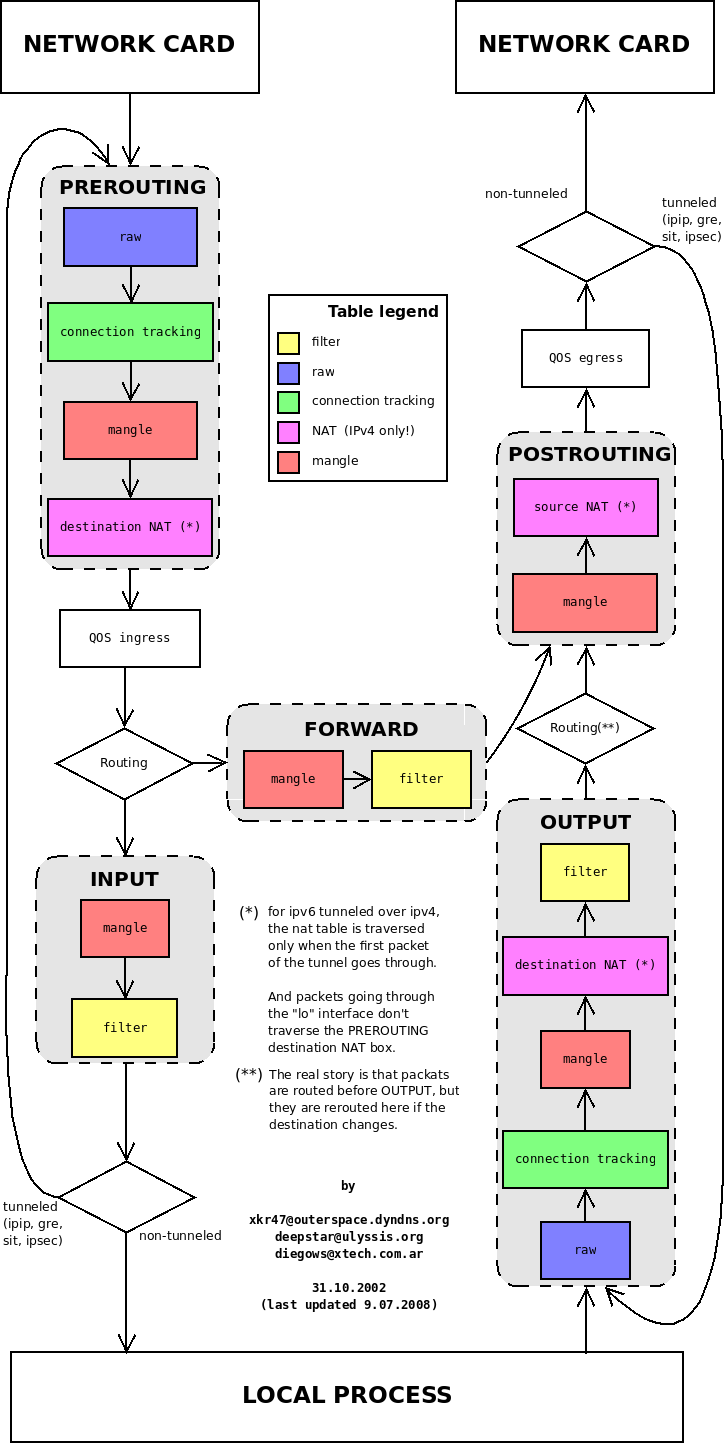
默认实现了 4 表、5 链
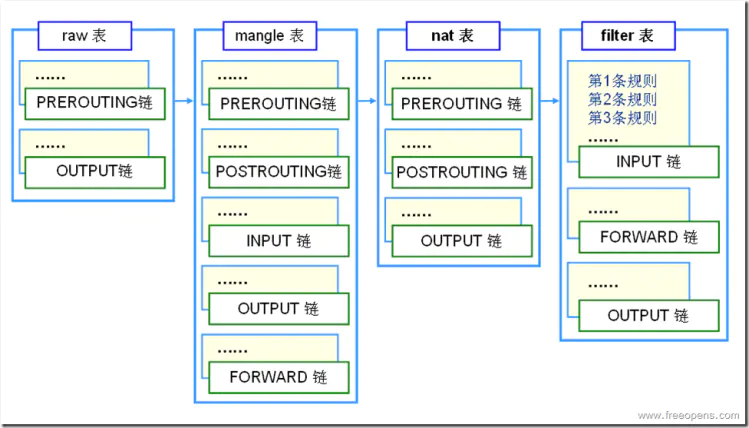
- raw:用于在其他表之前进行操作,可以避免 connection tracking
- filter:专门用于 filtering packets,如进行 DROP, LOG, ACCEPT or REJECT
- nat:用于网络地址转换,如端口转发
- 不应该在 nat table 上进行 filter,因为 nat 只会对一个流中的第一个 packet 进行处理,其它的包已经没有了 TCP Header(IP 层进行了分片)。nat table is only traversed by the first packet in a connection
-
mangle:用于修改 packet 的 header 信息,如 TTL, TOS。或者在内核空间给 packet 打上标记 (MARK),其他程序可以通过该 mark 进行其他操作。
TTL 的奇妙作用,ISP 单连接多计算机检测:The TTL target is used to change the TTL (Time To Live) field of the packet. We could tell packets to only have a specific TTL and so on. One good reason for this could be that we don't want to give ourself away to nosy Internet Service Providers. Some Internet Service Providers do not like users running multiple computers on one single connection, and there are some Internet Service Providers known to look for a single host generating different TTL values, and take this as one of many signs of multiple computers connected to a single connection.
- security: is used for Mandatory Access Control networking rules (e.g. SELinux -- see this article for more details)
通常只需要使用 filter 和 nat 表,mangle 表用于更复杂的操作。
iptables 命令¶
-
格式
- 不指定-t 时,默认指定 filter 表
命令选项¶
查看、添加、删除指定 table 指定 chain 中的规则 (rule)
- -L chain: 列出指定链中所有的规则进行查看
- -A chain rule-specification: 在指定链 chain 的末尾插入指定的规则,也就是说,这条规则会被放到最后,最后才会被执行。规则是由后面的匹配来指定。
- -I chain [rulenum] rule-specification: 在链 chain 中的指定位置插入一条或多条规则。如果指定的规则号是 1,则在链的头部插入。这也是默认的情况。
- -D chain rulenum: 在指定的链 chain 中删除一个或多个指定规则。
- -R rulenum:替换/修改第几条规则
创建、删除新链
- -N, --new-chain chain 用指定的名字创建一个新的链。
- -X, --delete-chain [chain] :删除指定的链,这个链必须没有被其它任何规则引用,而且这条上必须没有任何规则。如果没有指定链名,则会删除该表中所有非内置的链。
- -F, --flush [chain] 清空指定链 chain 上面的所有规则。如果没有指定链,清空该表上所有链的所有规则。
- -E, --rename-chain old-chain new-chain:用指定的新名字去重命名指定的链。这并不会对链内部造成任何影响。
- -Z, --zero [chain] :把指定链,或者表中的所有链上的数据包计数器和流量计数器归零。
- -P, --policy chain target:为指定的链 chain 设置策略 target。注意,只有内置的链才允许有策略,用户自定义的是不允许的。
匹配选项¶
- -i:指定数据包从哪个接口进入
- -o:指定数据包从哪个网络接口输出
- -p:指定数据包匹配的协议
- -s:指定数据包匹配的源地址
- -sport <源端口号>:指定数据包匹配的源端口号,可以使用[起始端口号:结束端口号]的格式指定一个范围的端口
- -d:指定数据包匹配的目标地址
- -dport <目标端口号>:指定数据包匹配的目标端口号,可以使用[起始端口号:结束端口号]的格式指定一个范围的端口
- !: 否定修饰
p.s. 还有更高级的匹配选项,如 Conntrack 匹配
动作选项¶
iptables(8) - Linux man page (die.net)
p.s 许多动作 (target) 只适用于特定的 table 和 chain 中,需要注意
- ACCEPT:接收数据包
- DROP:丢弃数据包
- REJECT:丢弃数据包,并响应 ICMP 错误信息
- RETURN:让规则遍历停止,或则返回上一条链
- LOG:日志功能,将符合规则的数据包的相关信息记录在日志中,以便管理员的分析和排错
NAT 相关¶
-
SNAT:修改 packet 的源地址,即我们常用的 NAT 功能
- 适用范围:nat 表,postrouting 链
-
MASQUERADE
- 适用范围:nat 表,postrouting 链 不用指定--to-source,用于动态获得地址(如 dhcp、pppoe)的情况,静态地址应该使用 SNAT。
-
DNAT:用于改变目的地址(和端口)
- 适用范围:nat 表,prerouting, output 链
- REDIRECT:将目的地址改编为本机(输入接口的主地址,如果为本机产生的包则为 127.0.0.1)
- 适用范围:nat 表,prerouting, output 链
MARK¶
-
MARK: The MARK target is used to set Netfilter mark values that are associated with specific packets. This target is only valid in the mangle table, and will not work outside there.
For example, we may set mark 2 on a specific stream of packets, or on all packets from a specific host and then do advanced routing on that host, to decrease or increase the network bandwidth, etc.
-
CONNMARK: The CONNMARK target is used to set a mark on a whole connection, much the same way as the MARK target does.
其它¶
list table¶
保存和恢复¶
持久化¶
iptables 配置持久化 — Cloud Atlas 0.1 文档 (cloud-atlas.readthedocs.io)
重置 rule¶
参考资料¶
- iptables - ArchWiki (archlinux.org)
- 最全资料:https://www.frozentux.net/iptables-tutorial/iptables-tutorial.html
- 其中介绍各个 table 和 chain 是如何遍历的:Iptables Tutorial 1.2.2 (frozentux.net)
- Iptables REDIRECT vs. DNAT vs. TPROXY – What I've learned during GSoC – Here I describe what I've learned during contributing to the netfilter project during my GSoC participation in 2018 hoping that it will help others looking for hard-to find information. (ecklm.com)
- 本地进程产生的包在 output chain 之前进行一次路由,得到 src ip。之后如果进行了 dnat,则会重新进行路由。Linux netfilter Hacking HOWTO: Netfilter Architecture
- 写得很好:netfilter 数据流图 | C0reFast 记事本 (ichenfu.com)